Figure 6. Ir56b has a conserved function and an atypical structure.
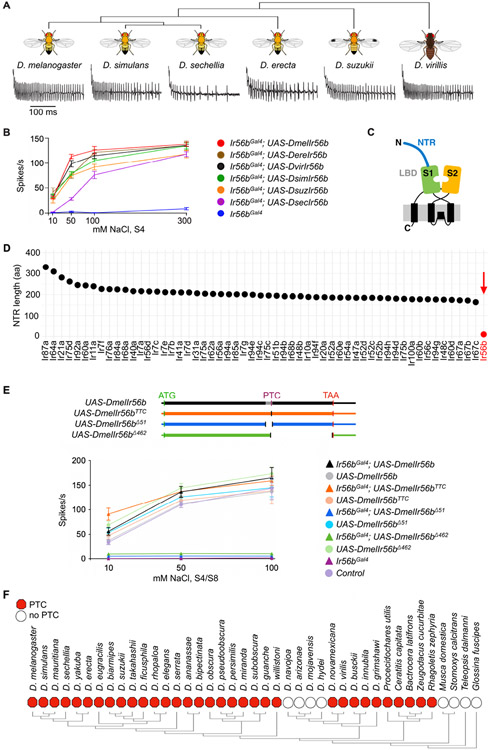
(A) Electrophysiological traces from D. melanogaster IR56bGal4; UAS-DxIr56b, where x represents each of the indicated species. Recordings were from S4 sensilla tested with 50 mM NaCl.
(B) Responses of S4 sensilla to NaCl in each of the indicated genotypes. n= 5-10. Error bars = S.E.M.
(C) Diagram of tuning IRs, showing N-terminal region (NTR), and the S1 and S2 half-domains of the LBD. Adapted from Abuin et al. (2019).
(D) Length of the N-terminal regions of all tuning IRs (all Irs except Ir8a, Ir25a, Ir76b, and Ir93a, which are considered co-receptors17).
(E) The variant D. melanogaster Ir56b UAS constructs tested (top). All constructs include untranslated regions (thin boxes), the start codon (ATG), and the normal termination codon (TAA). The UAS-DmelIr56bTTC construct lacks the premature termination codon (PTC) and replaces it with a TTC codon, the UAS-DmelIr56bΔ51 construct lacks the annotated intron (grey), and the UAS-DmelIr56bΔ462 construct lacks the coding sequence from the PTC until the TAA, which it includes. Responses of S4/S8 sensilla to NaCl in each of the indicated genotypes (bottom). n= 5-10. Error bars = S.E.M.
(F) Presence (red hexagon) or absence (empty circle) of the PTC in the 41 IR56b orthologs identified through BLAST searches.
See also Figures S4-S6, Table S1 and Table S2.