Figure 5. Niche cells are polarized during assembly.
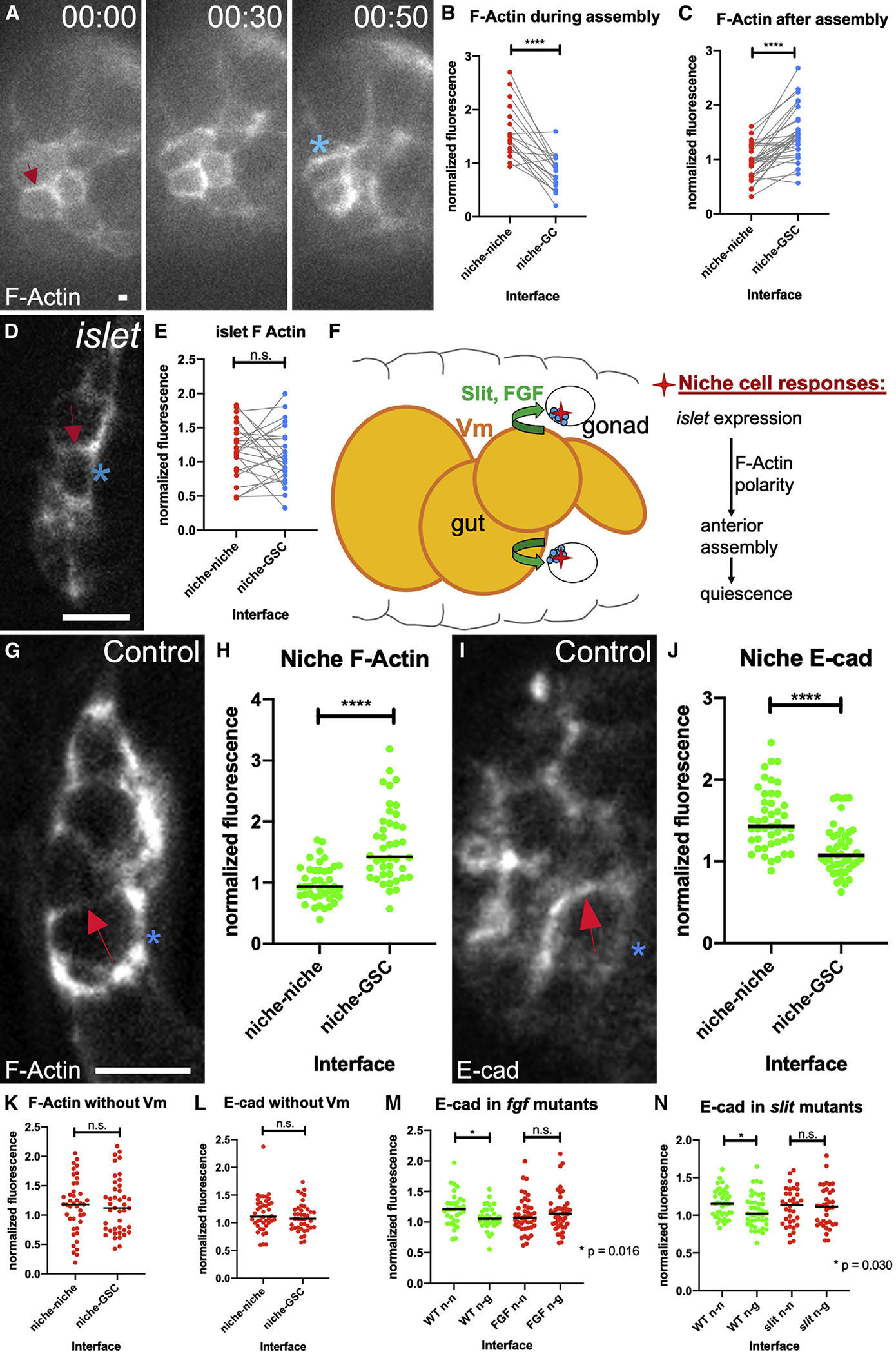
(A) Stills from a time course of a gonad expressing six4-eGFP::moesin to label F-actin in all SGPs. F-actin accumulates at niche-niche interfaces when niche cells begin to associate (arrow), and later repolarizes to niche-stem cell interfaces (asterisk).
(B and C) Quantification of F-actin accumulation at niche-niche or niche-germ cell interfaces (B) during and (C) after completion of niche assembly in fixed tissue (p < 0.0001, Wilcoxon test).
(D) Niche cells in fixed tissue expressing a somatic cell F-actin label, six4-eGFP::moesin in islet mutants in which niche cells have begun to associate but have not completed assembly.
(E) F-actin accumulation at niche cell interfaces in islet mutants.
(F) A model illustrating how Vm signals influence niche assembly.
(G and I) Niche cells from fixed Stage 17 control gonads (G) expressing six4-eGFP::moesin or (I) immunostained for E-cadherin.
(H) F-actin accumulation at niche-GSC interfaces versus niche-niche interfaces (p < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney test).
(J) E-cadherin accumulates at niche-niche interfaces compared with niche-GSC interfaces (p < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney test).
(K–N) Quantification of polarity loss in Stage 17 niches for (K) F-actin in biniou, (L) E-cadherin in biniou, (M) Ecad with pyr and ths removed (fgf), or (N) Ecad in slit mutants (Mann-Whitney tests). Asterisks, niche-GSC interfaces; arrows, niche-niche interfaces. Scale bars, 5 μm.
