Figure 1. Endocrine control of Metabolism.
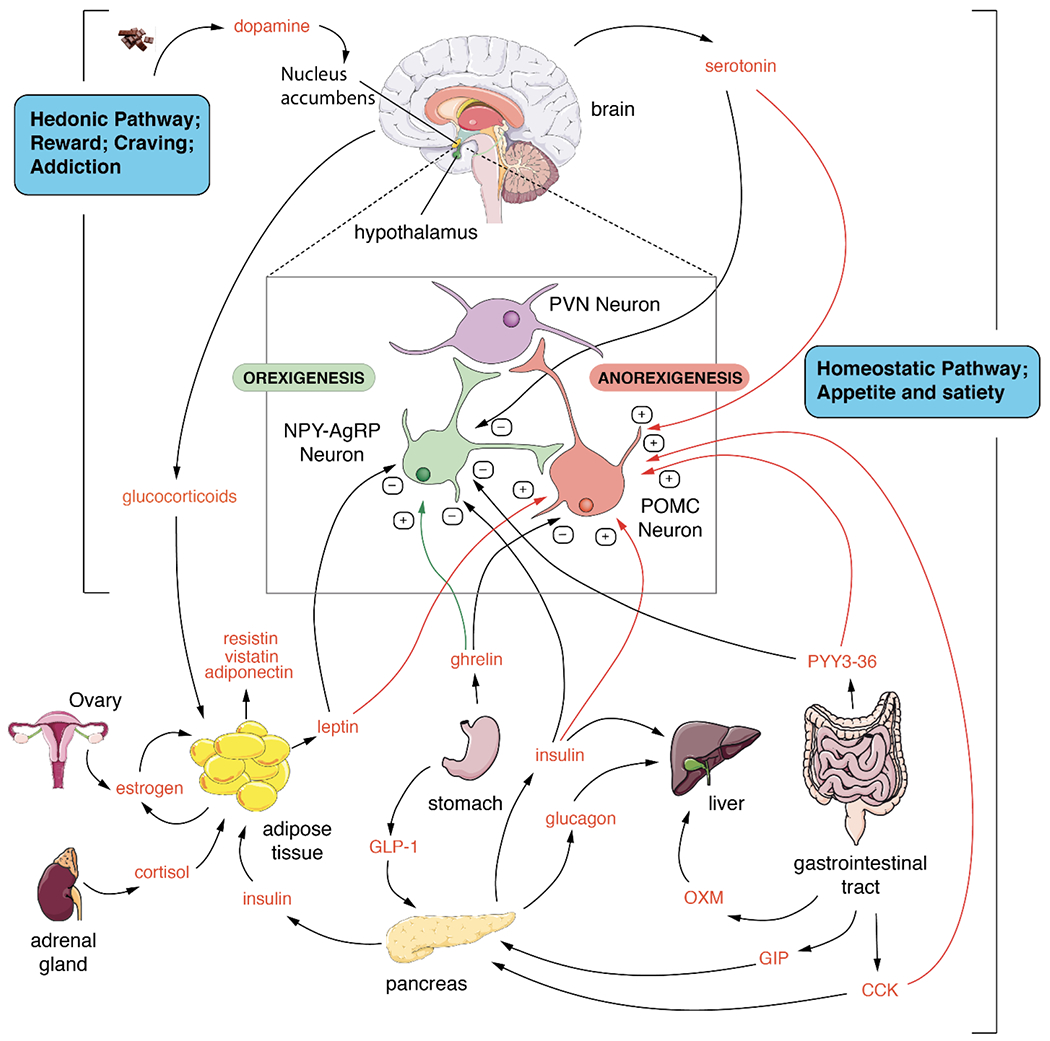
The main tissues involved in controlling metabolism are shown along with the main endocrine and paracrine modulators of metabolic function. Many positive and negative control points in the tissues and the brain are integrated to control metabolism and body weight. The homeostatic pathway is the largest and most complex and likely regulates the set point for metabolism via control of the appetite and satiety centers in the brain. The hedonic center controls emotional eating and food addiction which can override the homeostatic system.
