Figure 2. The interplay between leptin and insulin signaling pathways.
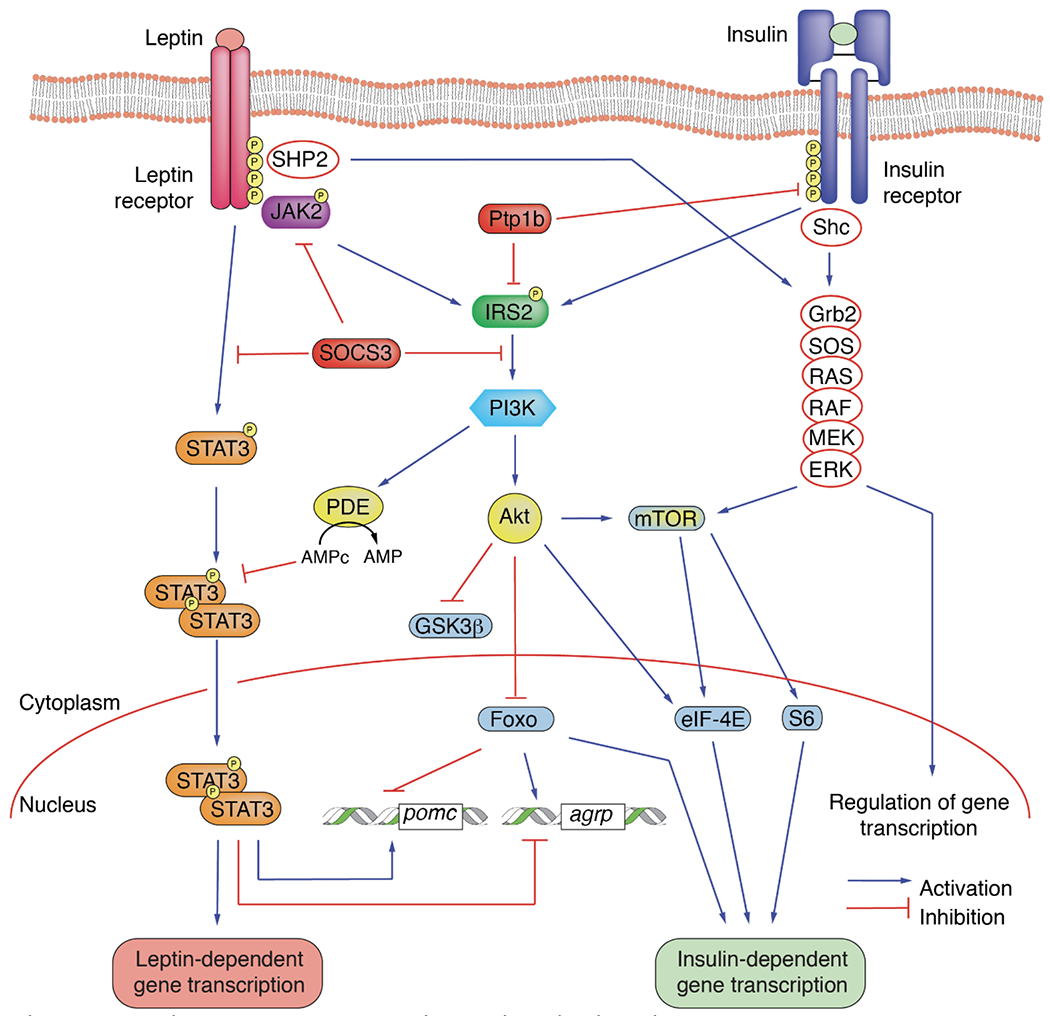
The insulin receptor and the leptin receptor recruit the low-abundance-message insulin receptor substrate-2. Lack of available insulin receptor substrate 2 for the leptin receptor due to hyperinsulinemia could result in defective leptin signal transduction. Alternatively, insulin induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 could inactivate the leptin receptor through alterations in tyrosine phosphorylation.
Abbreviations, Agrp: Agouti-Related Neuropeptide; Akt: AKR Thymoma, protein kinase B; eIF-4E: Eukaryotic translation Initiation Factor 4E; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated Kinase; Foxo: Forkhead box; Grb2: Growth factor receptor-Bound protein 2; GSK3β: Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3-beta; IRS2: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2; JAK2: Janus Kinase 2; MEK: MAPK/ERK Kinase; mTOR: mammalian Target Of Rapamycin; PDE Phosphodiesterase; PI3K: PhosphatidylInositol 3-Kinase; pomc: Proopiomelanocortin; Ptp1b: Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B; RAF: Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma kinase; RAS: Rat Sarcoma virus protein; S6: S6 ribosomal protein; Shc: Src homology 2 domain-containing; SHP2: Src Homology region 2-containing Protein tyrosine phosphatase 2; SOCS3: Suppressor Of Cytokine Signaling 3; STAT3: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3
