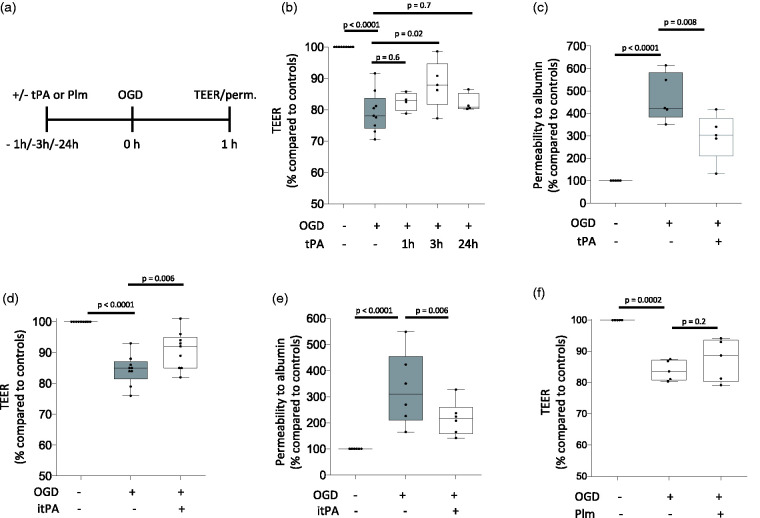
Figure 2.
Effect of preconditioning with tPA on the permeability of the blood-brain barrier. a. Diagram depicting the experimental paradigm to study the effect of tPA and plasmin (Plm) on the permeability of an in vitro model of the blood brain barrier (BBB), assembled by brain microvascular endothelial cells and astrocytes co-cultured on both sides of a 1 μm pore size insert. b. The in vitro model of the BBB described in A was exposed to 60 minutes of oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) conditions either 1 (n = 15 inserts assembled with cells from 4 different cultures), or 3 (n = 12 inserts assembled with cells from 5 different cultures), or 24 hours (n = 10 inserts assembled with cells from 4 different cultures) after treatment with 5 nM of tPA. A subgroup of inserts was kept under physiological conditions (n = 16, assembled with cells from 9 different cultures). Values depict the transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) in inserts exposed to OGD conditions compared to the TEER in inserts maintained under normoxic conditions. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. c. The in vitro model of the BBB described in A was treated with 5 nM of tPA (n = 13 inserts assembled with cells from 5 different cultures), or vehicle (control; n = 12 inserts assembled with cell from 5 different cultures) 3 hours before exposure to 60 minutes of OGD. The permeability to albumin in inserts exposed to OGD conditions was compared to the permeability of inserts maintained under normoxic conditions (n = 11, assembled with cells from 5 different cultures). Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons test. d. TEER of the in vitro model of the BBB described in A and treated with either 5 nM of proteolytically inactive tPA (itPA; n = 19 inserts assembled with cells from 9 different cultures), or vehicle (control; n = 18 inserts assembled with cells from 9 different cultures) 3 hours before 60 minutes of OGD. Data were compared to the TEER in inserts maintained under normoxic conditions (n = 19, assembled with cells from 9 different cultures). Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Holms-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. e. Permeability to albumin in the in vitro model of the BBB described in A and treated with either 5 nM of proteolytically inactive tPA (itPA; n = 18 inserts assembled with cells from 5 different cultures), or vehicle (control; n = 17 inserts assembled with cells from 6 different cultures) 3 hours before exposure to 60 minutes of OGD. In each case data were compared to permeability to albumin in inserts maintained under normoxic conditions (n = 17, assembled with cells from 6 different cultures). Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Holms-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. f. TEER of the in vitro model of the BBB described in A and treated with either 100 nM of plasmin (Plm; n = 10 inserts assembled with cells from 5 different cultures), or vehicle (control; n = 10 inserts assembled with cells from 5 different cultures) three hours before exposure to 60 minutes of OGD. In each case data were compared to the TEER of inserts maintained under normoxic conditions (n = 9 inserts assembled with cells from 5 different cultures). Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Holms-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test.