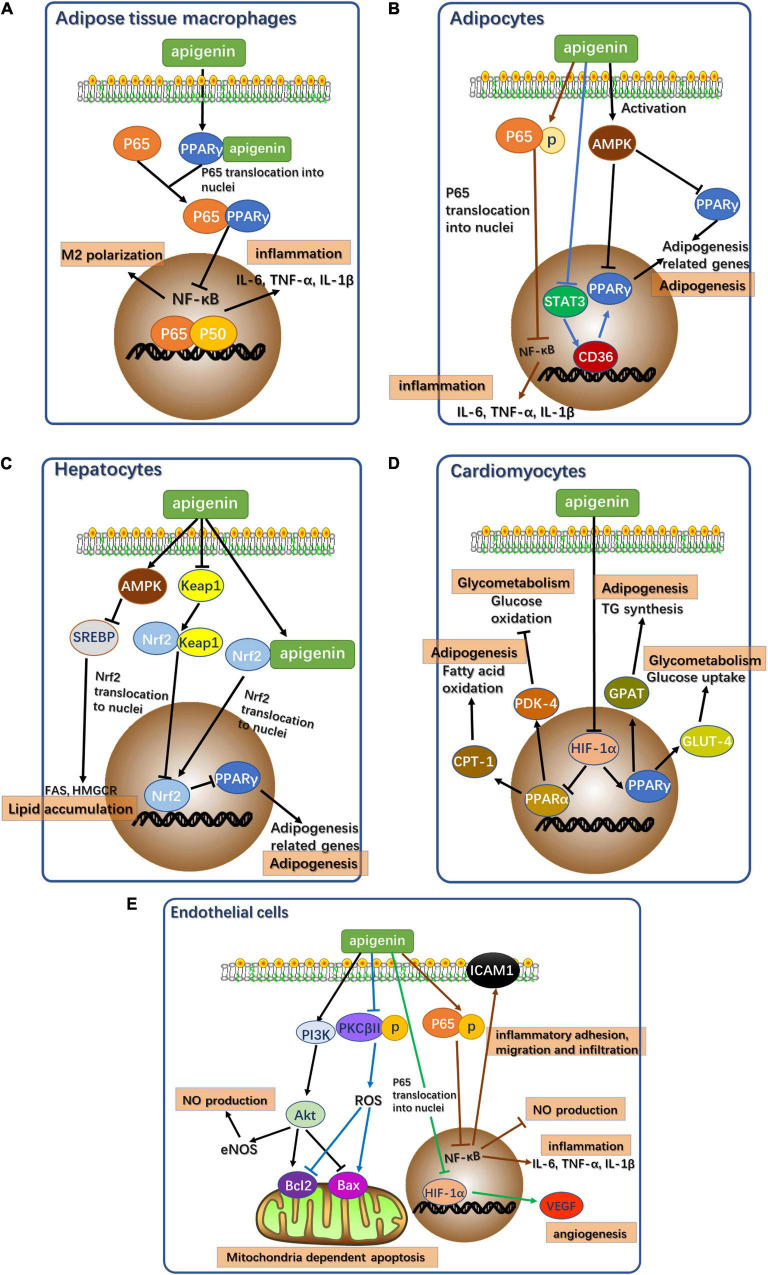
FIGURE 2.
Potential signaling pathways of apigenin affecting cardiometabolic diseases in different types of cells. (A) Potential signaling pathways of apigenin affecting cardiometabolic diseases in adipose tissue macrophages. p65: RelA, NF-κB component. P50: p50 NF-κB component. (B) Potential signaling pathways of apigenin affecting cardiometabolic diseases in adipocytes. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase. p65: RelA, NF-κB component. STAT3, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. (C) Potential signaling pathways of apigenin affecting cardiometabolic diseases in hepatocytes. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase. SREBP, sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. FAS, fatty acid synthase. HMGCR, 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A Reductase. Keap1, Kelch like ECH associated protein 1. Nrf2, NF-E2-related factor 2. (D) Potential signaling pathways of apigenin affecting cardiometabolic diseases in cardiomyocytes. HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha; CPT1, carnitine palmitoyl transferase I; PDK4, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4; GPAT, glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase; GLUT4, glucose transporter type 4. (E) Potential signaling pathways of apigenin affecting cardiometabolic diseases in endothelial cells. PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; PKCβII, protein kinase C subunit β II; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax, Bcl2 associated X; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; p65, RelA, NF-κB component.