FIGURE 3.
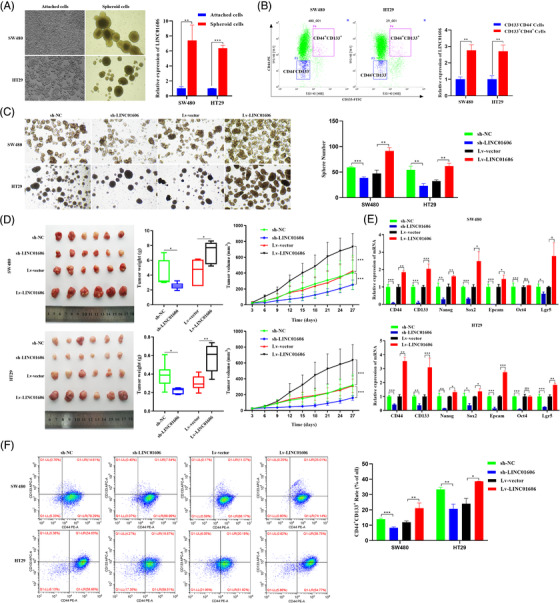
LINC01606 enhances the stemness of colon cancer cells. (A) Representative images of adherent cells and the tumour spheres. The expression level of LINC01606 in adherent cells and tumour spheres was detected by qRT‐PCR (n = 3). (B) Cells were double stained with anti‐CD44‐PE and anti‐CD133‐FITC. Flow cytometry fluorescent cell sorting was used to attain CD44+CD133+ and CD44−CD133− colon cancer cells. The expression level of LINC01606 in CD44+CD133+ and CD44−CD133− colon cancer cells was detected by qRT‐PCR (n = 3). (C) Tumour sphere formation of SW480 and HT29 cells after transfected with sh‐ LINC01606‐expressing vector or LINC01606‐expressing vector. (D) Representative images of tumours in xenograft mouse models bearing SW480 and HT29 cells transfected with sh‐LINC01606‐expressing vector or LINC01606‐expressing vector. The tumour volumes were measured every 3 days and the tumour weights were measured after 4 weeks when mice were sacrificed (n = 6). (E) The effect of LINC01606 on colon cancer cell stem‐like markers. CD44, CD133, Nanog, Sox2, Epcam, Oct4, and Lgr5 levels were analysed by qRT‐PCR after transfected with LINC01606 shRNA‐expressing vector or LINC01606‐expressing vector (n = 3). (F) Flow cytometry analysis of the quantity of CD44+CD133+ cells in SW480 and HT29 after transfected with LINC01606 shRNA‐expressing vector or LINC01606‐expressing vector (n = 3). Data are shown as the mean ± SD. *p < .05, **p < .01 and ***p < .001 compared with control
