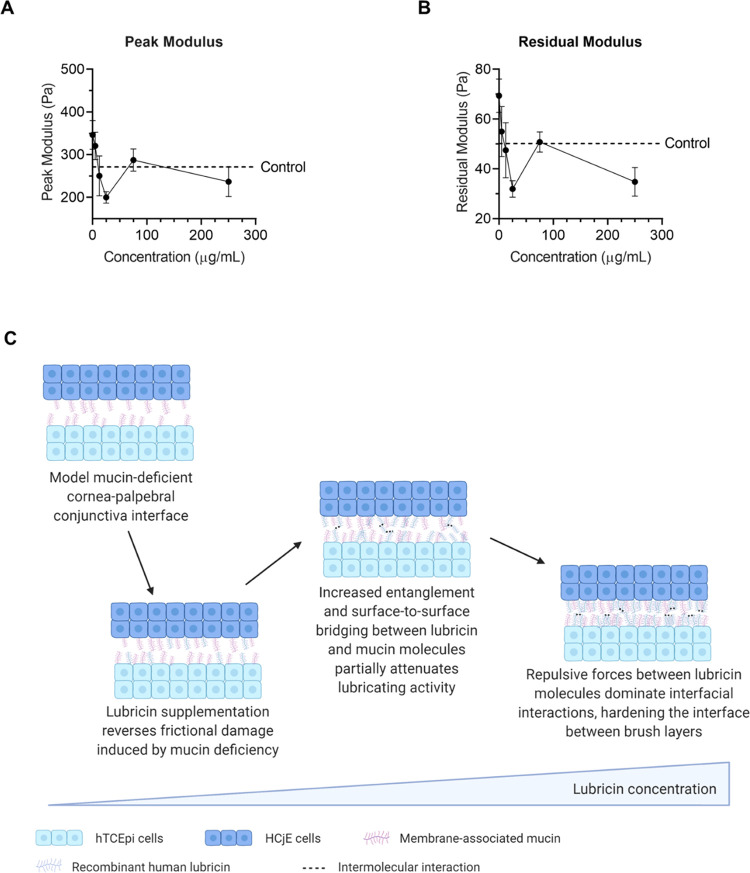
Figure 4.
Recombinant human lubricin exhibited dose-dependent biolubrication properties at model mucin-deficient cornea–palpebral conjunctiva interfaces. (A) Peak modulus exhibited a concentration-dependent response (p < 0.0029) to lubricin supplementation (data = mean ± SE, n = 7–13). (B) Lubricin supplementation also reduced the residual modulus in a dose-dependent manner (p < 0.0011) (data = mean ± SE, n = 7–13). (C) Idealized schematic showing possible mechanism behind observed dose-dependent biolubrication effects at dry eye mimetic ocular surfaces. Statistical significance (p < 0.05) was determined using one-way Welch's ANOVA (A, B).