Figure 26.
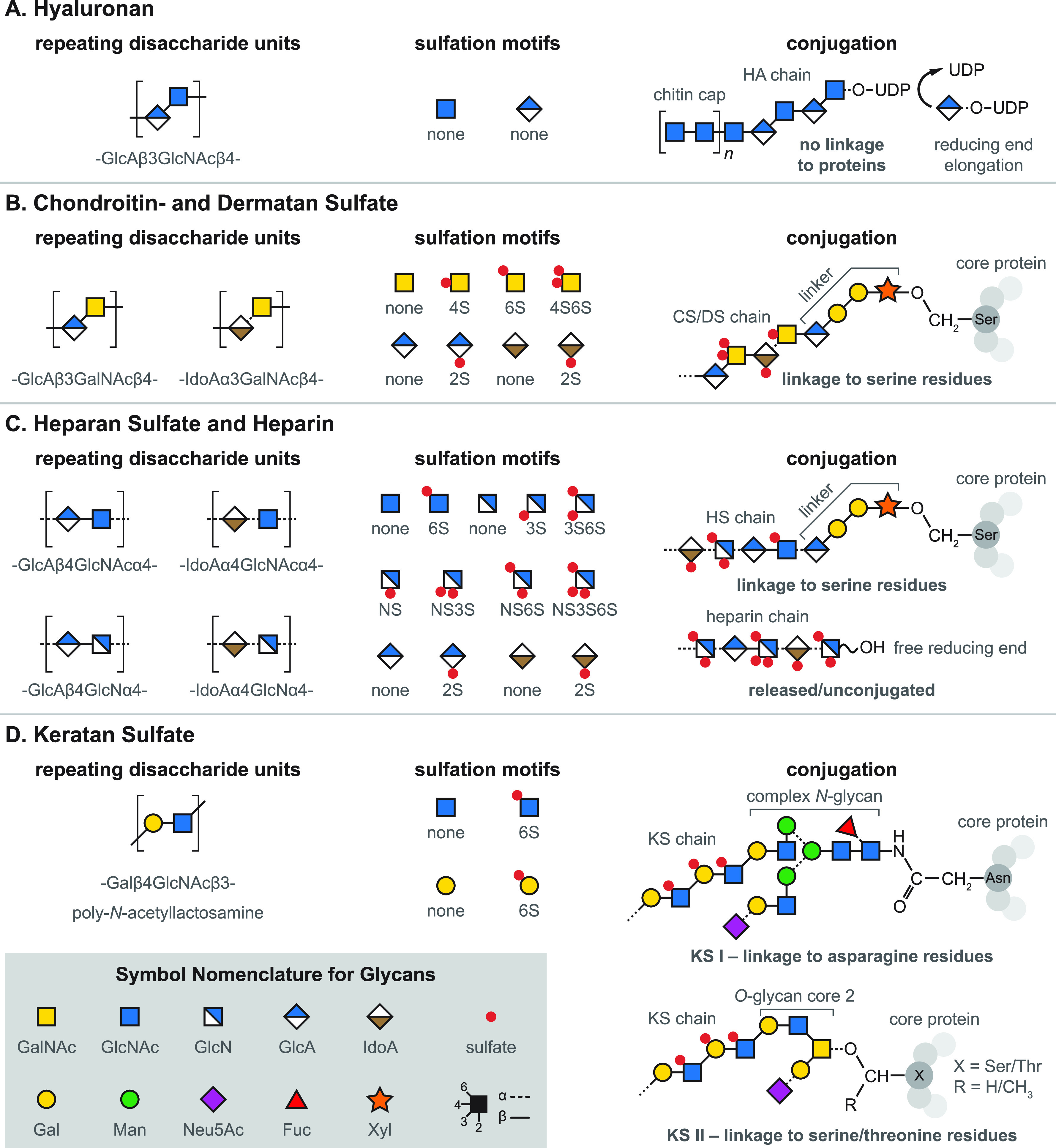
General structure of glycosaminoglycans. Overview of the characteristic disaccharide units, sulfation motifs, and potential protein linkages found in the four main glycosaminoglycan families. (A) Repetitive hyaluronan chains are not modified further by sulfation or epimerization. Uniquely, biosynthesis starts with the formation of a chitin cap and proceeds toward the reducing end. (B) Chondroitin and dermatan sulfate display a variety of sulfation motifs. The chains are linked to serine residues of proteoglycan core proteins through a specific tetrasaccharide linker. (C) Heparan sulfate and heparin represent the most diverse family of glycosaminoglycans. The heparin chain depicted corresponds to the antithrombin III binding sequence, mimicked by the synthetic anticoagulant fondaparinux. Discovery of additional sulfation motifs in the future cannot be ruled out. (D) Keratan sulfate contains galactose instead of hexuronic acid. The chains may be linked to both asparagine and serine/threonine residues of core proteins.
