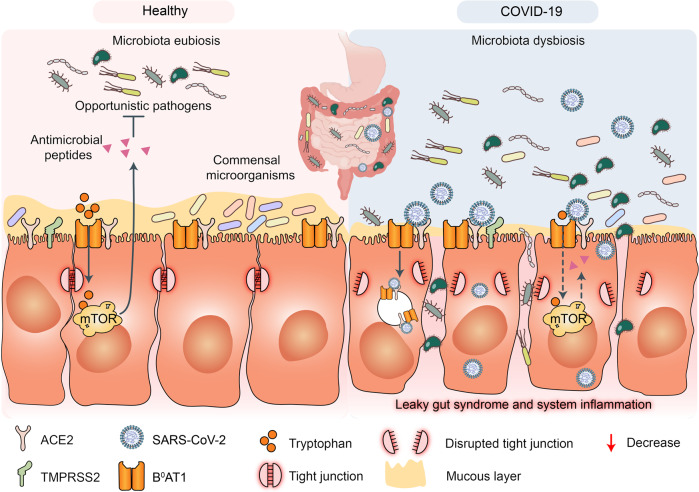
Fig. 4.
Potential mechanisms of cytokine storm and secondary pathogen infections resulting from gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with COVID-19. Gut microbiota are also disrupted by SARS-CoV-2 infection which potentially triggers cytokine storm and secondary pathogen infections. B0AT1 mediates neutral amino acid uptake by luminal surfaces of intestinal epithelial cells. It is also a molecular ACE2 chaperone. B0AT1 substrates such as tryptophan and glutamine activate antimicrobial peptide release, promote tight junction (TJ) formation, downregulate lymphoid proinflammatory cytokines, and modulate mucosal cell autophagy via mTOR signaling. As ACE2 is a molecular B0AT1 chaperone, ACE2-associated B0AT1 may be internalized during SARS-CoV-2 infection, decrease B0AT1 on cell membranes, promote gut opportunistic pathogen invasion, facilitate cytokine storms, and exacerbate COVID-19