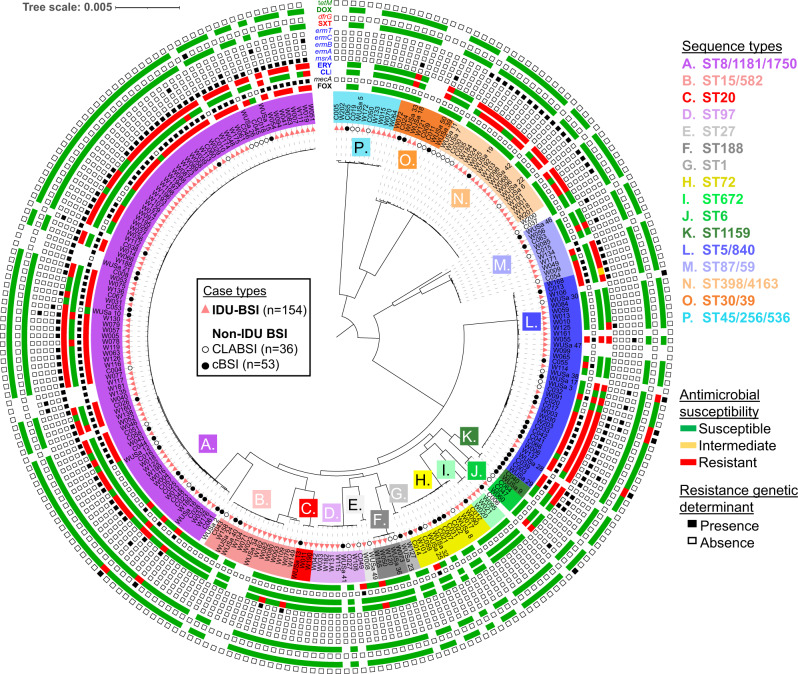
Fig. 3. Phylogeny of BJH S. aureus BSI isolates.
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree is based on 86493 core genome SNPs and rooted to midpoint. Black-filled circles, unfilled circles and red triangles on branch tips denote cBSI, CLABSI and IDU-BSI isolates, respectively. Isolate names are highlighted with colors denoting the multilocus sequence type (ST) identity of each isolate. Single and double-locus variant STs that exclusively share a common ancestor, are grouped in 16 ST groups. Outer rings denote an isolate’s antibiotic susceptibility according to electronic medical records (multicolored strip) and the presence/absence of attributable genetic determinants according to WGS (adjacent squares). Antibiotic and gene name labels are color coded according to pertinent antibiotic class. FOX, cefoxitin; CLI, clindamycin; ERY, erythromycin; SXT, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole; DOX, doxycycline. Figure metadata included in Supplementary Data 3.