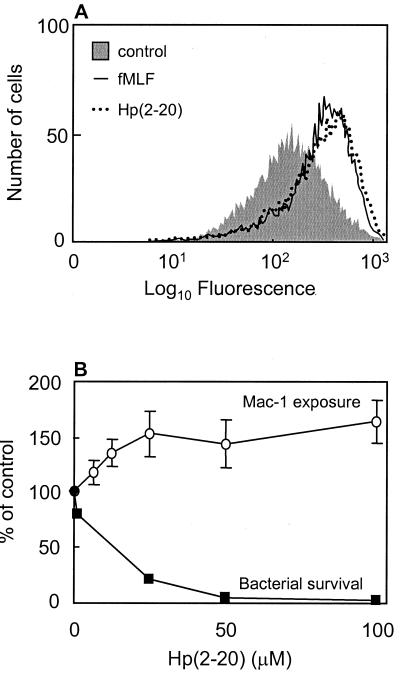
FIG. 1.
Neutrophil activation and bactericidal effect of Hp(2-20). (A) Hp(2-20) induces Mac-1 mobilization in human neutrophils. Surface exposure of the integrin Mac-1 on neutrophils after stimulation with Hp(2-20) (100 μM; dotted line) and fMLF (50 nM; solid line) are shown as histograms from a representative FACScan analysis. (B) Hp(2-20) induced Mac-1 mobilization in a dose-dependent manner at concentrations similar to those required for a prominent antibacterial effect. The relative increases in Mac-1 surface exposure (open circles) were calculated from the mean fluorescence intensities of cells activated with different concentrations of Hp(2-20) and are expressed as percentages of the value obtained with unstimulated cells. The results are given as means ± standard deviations (n = 4). The surviving fraction of E. coli after 15 min of incubation with the indicated Hp(2-20) concentrations (closed boxes) is also shown (representative experiment), demonstrating the bactericidal effect of the peptide.