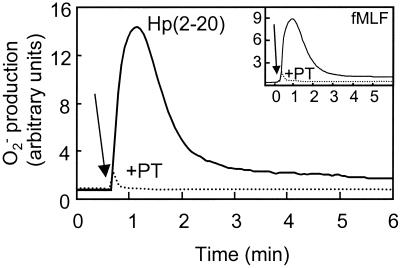
FIG. 3.
Hp(2-20)-induced activation of the neutrophil NADPH-oxidase. Hp(2-20) induces superoxide anion production with kinetics resembling the kinetics of fMLF-induced superoxide anion production. Pertussis toxin completely abolishes activation of the neutrophil NADPH-oxidase, indicating that the activation is dependent on signaling via a G-protein-coupled receptor. Neutrophils were preincubated at 37°C for 60 min in the absence (solid line) or presence (dotted line) of pertussis toxin (PT 500 ng/ml) and were then stimulated with Hp(2-20) (100 μM) or fMLF (50 nM; inset). The superoxide anion release was measured by isoluminol-enhanced chemiluminescence (11). The arrows indicate the addition of peptide.