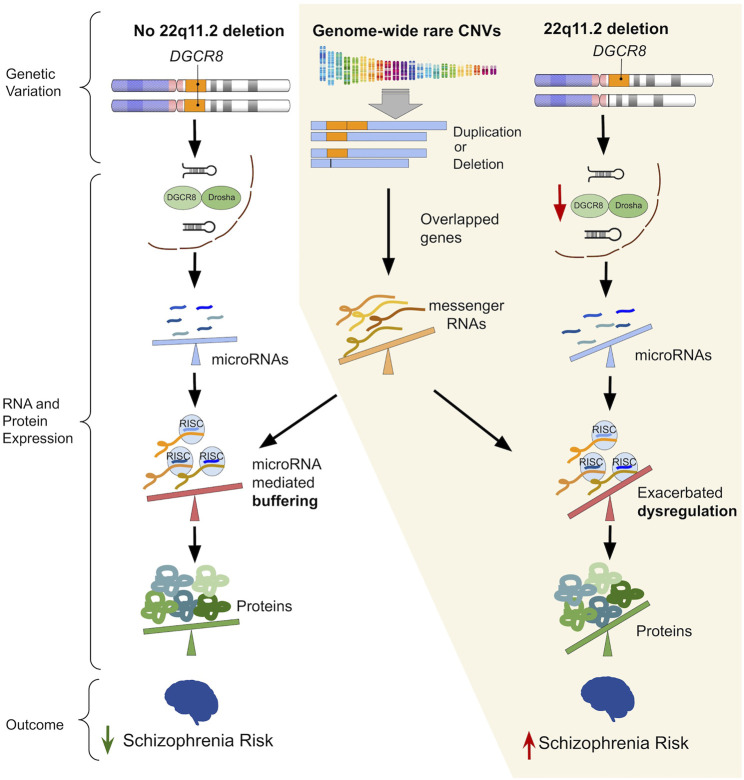
FIGURE 1.
The left-hand column (“No 22q11.2 deletion”) illustrates the ability of an intact microRNA (miRNA) regulatory system to buffer the effects of genetic variation that would otherwise perturb gene expression. The parts grouped by the yellow background illustrate the proposed mechanism of how widespread miRNA dysregulation imparted by the 22q11.2 deletion may exacerbate the downstream impact of rare genome-wide copy number variants (CNVs), thereby increasing risk for schizophrenia. Hemizygosity of DGCR8 due to the 22q11.2 deletion leads to reduced processing of primary-to pre-miRNAs in miRNA biogenesis, thus resulting in widespread miRNA dysregulation. Subsequently, an altered degree of miRNA targeting of differentially expressed messenger RNA (mRNA) transcripts (due to overlapping rare CNVs) may amplify dysregulation of protein expression. A steeper tilt of the seesaws represents a greater degree of dysregulation (i.e., upregulation or downregulation) of miRNAs, mRNAs, proteins, or miRNA mediated repression/degradation of its target mRNA.