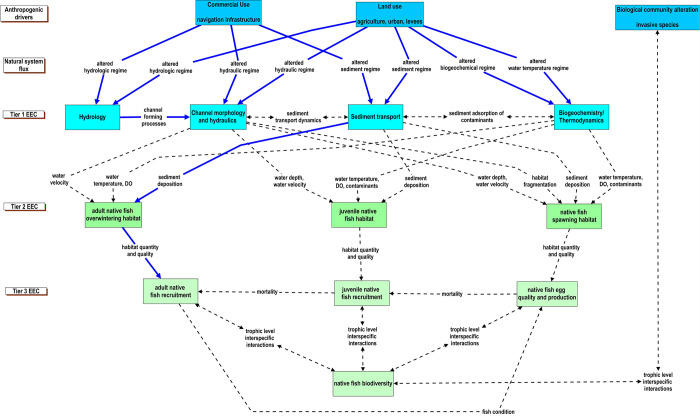
Fig 8. Conceptual model of how anthropogenic drivers in the upper Mississippi and Illinois Rivers influence native fish habitats and recruitment.
Essential ecosystem characteristics (EECs) are groupings of ecosystem components. Tier 1 EECs represent physical and chemical effects; fundamental measures of process that are directly affected by anthropogenic and natural drivers. Tier 2 EECs represent a broad habitat category that is intended to encompass the physical, chemical, and biological components of the riverine habitats that influence reproduction, growth, and survival of biotic communities. The Tier 3 EECs represent components of the biological systems that respond to changes in the hierarchical components of the conceptual model. The strength of our understanding of the relationships of how natural and anthropogenic drivers interact with habitats, biological systems, and fish in large rivers is represented by the different types of lines in the figure. Solid blue lines depict a strong understanding of the relationship, the dotted-dashed blue line represents a moderate understanding of the relationship, and the black dashed line represents a weak understanding of the relationship. The different types of lines also represent the strength of our understanding of within EEC-tier relationships.