Figure 1.
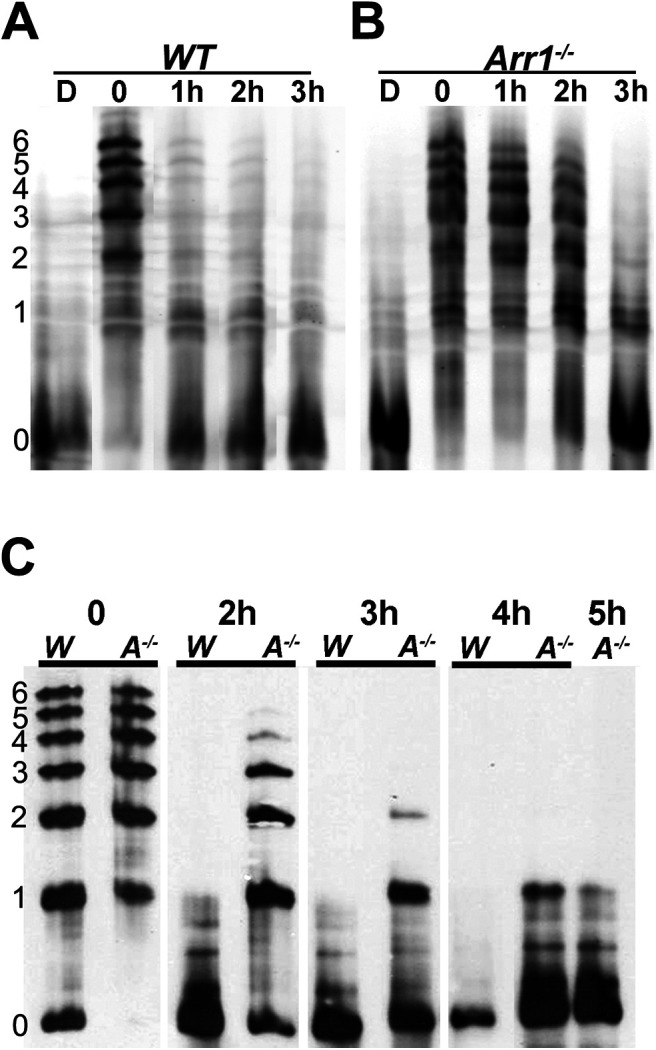
Rhodopsin dephosphorylation is delayed in retinae of Arr1−/− mice. Differently phosphorylated species of rhodopsin were separated by IEF followed by Western blotting. Left, The number of phosphates on rhodopsin. A, WT and (B) Arr1−/− mice were dark-adapted (D) or exposed to light and returned to darkness for the indicated times (0-3 h). Immediately after light exposure (0), most of the rhodopsin shifted to phosphorylated species (1-6 phosphates). Levels of the phosphorylated species were greatly reduced in WT, but not Arr1−/−, after 1 h of dark adaptation. C, Comparison of WT (W) and Arr1−/− (A−/−) rhodopsin phosphorylation status on a longer time scale (0-5 h).
