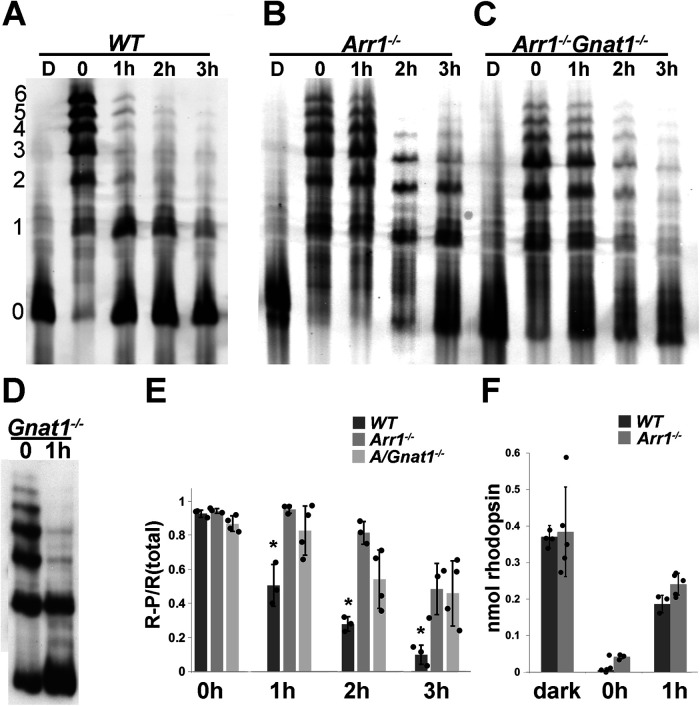
Figure 2.
Delayed rhodopsin dephosphorylation in retinae lacking ARR1 is not because of cell stress caused by persistent transducin signaling. The status of rhodopsin phosphorylation was examined using IEF in (A) WT mice, (B) Arr1−/− mice, (C) Arr1−/−Gnat1−/− mice, and (D) Gnat1−/− mice. E, Ratio of signals summed from all phosphorylated species (1-6) and all rhodopsin species (0-6 phosphates) as a function of time. Values indicate mean ± SD; N ≥ 3. One-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey's HSD showed no difference at 0 h, but a significant difference between WT and Arr1−/− and Arr1−/−/Gnat1−/− samples at 1, 2, and 3 h (p < 0.01). F, Quantification of the amount of total rhodopsin present per retina in dark-adapted (dark) and mice immediately after light exposure (0) and after 1 h in darkness (mean ± SD; N ≥ 3).