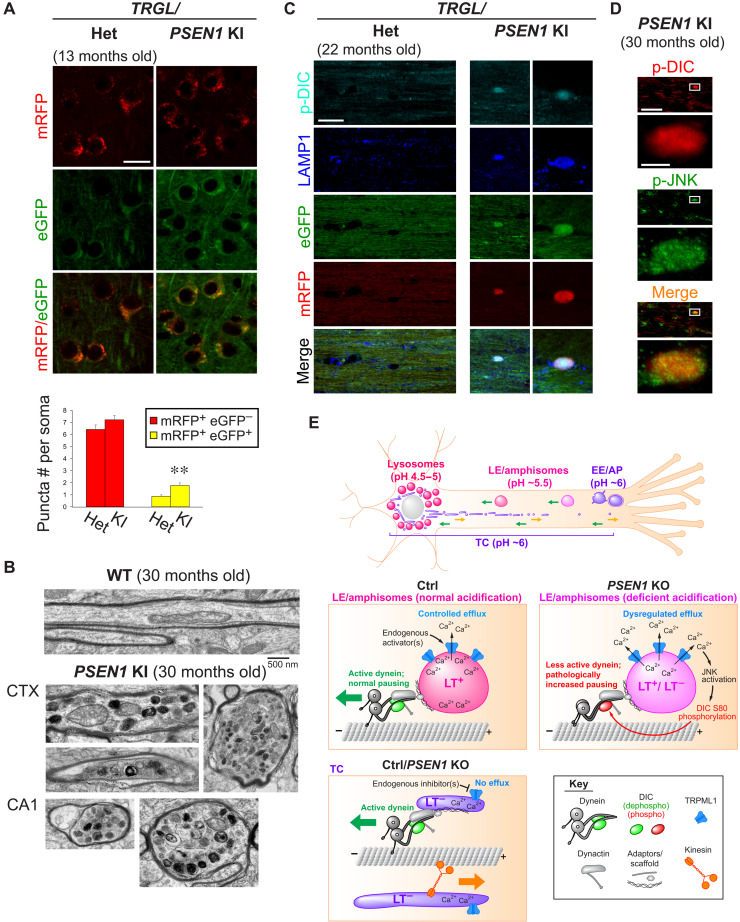
Fig. 8. Key axonal transport pathophysiology in PSEN1 KO neurons is recapitulated in brains of aged PSEN1-M146V KI mice modeling familial AD.
(A) Images of eGFP-mRFP-LC3 signal in heterozygous (het) versus homozygous PSEN1 KI/TRGL mouse brain cortex (13 months old). Graph shows numbers of robustly acidified (mRFP+ eGFP−) and poorly acidified (mRFP+ eGFP+) compartments. Bars = means + SEM (n = 234 and 254 somas in het and PSEN1 KI). **P < 0.01, Student’s t test. (B) Representative images of normal and dystrophic myelinated axons in 30-month-old wild-type (WT) and PSEN1 KI mouse brains. CTX, brain cortex; CA1, hippocampus CA1 region. (C) Coimmunostaining of p-DIC-S80 (pseudo-colored cyan) and LAMP1 (pseudo-colored blue) in corpus callosum of heterozygous versus homozygous PSEN1 KI/TRGL mouse brains (22 months old). (D) Coimmunostaining of p-DIC-S80 and p-JNK in corpus callosum of 30-month-old PSEN1 KI mouse brains. (E) Hypothetical model of physiological and pathological TRPML1-mediated regulation of LAMP1 vesicle axonal transport. Top overview image shows LAMP1 vesicle subpopulations with distinct acidification, distribution, and axonal transport behaviors. Green arrows, retrograde; orange arrow, anterograde. Immature early endosomes (EEs) and autophagosomes (APs) in distal axon mature into LEs/amphisomes that undergo continuous maturation and retrograde transport in midproximal axon, with fully acidic lysosomes restricted to soma. TGN-derived TCs undergo bidirectional transport. Middle: Axonal LEs/amphisomes are largely LAMP1+ LT+ in both Ctrl and PSEN1 KO, but some become insufficiently acidified (LT−) in PSEN1 KO. In Ctrl, despite high enrichment of TRPML1 on axonal LEs/amphisomes, the acidic lumen maintains low basal TRPML1 activity. Controlled Ca2+ efflux induced by endogenous agonists facilitates normal vesicle pausing. In PSEN1 KO, acidification failure in LEs/amphisomes causes dysregulated Ca2+ efflux, leading to JNK activation, DIC hyperphosphorylation, and impaired dynein activity characterized by excess pausing. Bottom: TRPML1 is inactive on highly motile TCs (LT−).