Figure 5.
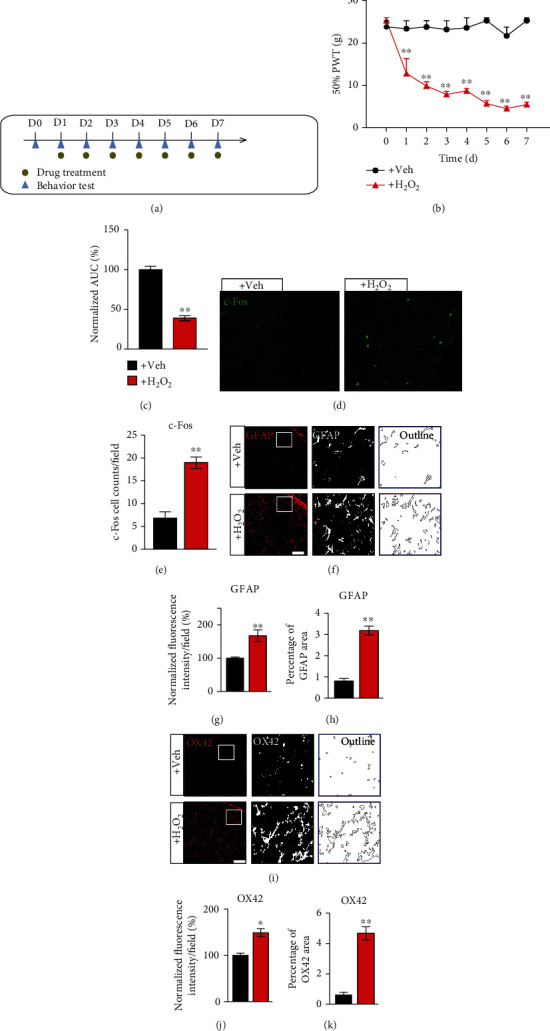
Locally increasing oxidative stress produces mechanical allodynia among naïve rats. (a) Schematic protocol showing time points for H2O2/vehicle treatment in naïve rats. (b) Time course of 50% PWT changes after H2O2/vehicle treatment. The +H2O2 group receives daily H2O2 (100 nmol/site) injection into hindpaws, whereas the +Veh group receives only vehicle (PBS) injection. (c) Summary of AUC as in (b). (d) Ipsilateral SCDH with c-Fos staining from the +Veh vs. +H2O2 group. (e) Summary of the number of c-Fos-positive cells per observation field. (f) Ipsilateral SCDH with GFAP staining. Summary of the normalized fluorescence intensity (%) of GFAP (g) and percentage of GFAP-stained area (h). (i) Ipsilateral SCDH with OX42 staining. Summary of the normalized fluorescence intensity of OX42 (j) and percentage of OX42-stained area (k). n = 6 rats/group. ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. +Veh group.
