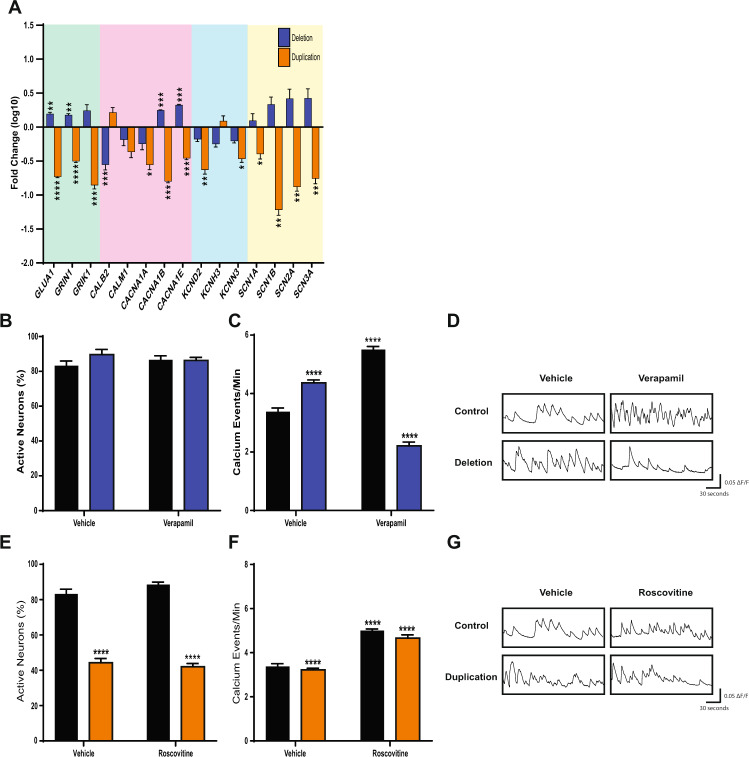
Fig. 5. Pharmacological modulation of L-type calcium channel rescues abnormal calcium activity in neurons with 1q21.1 deletions and duplications.
A Expression of key neuronal channels in 1q21.1 deletion and duplication neurons following 50 days of neuronal differentiation. The values are presented as fold change compared to expression in controls. Data were analysed using multiple T tests (n ≥ 3) and significance is based on Holm–Sidak corrected P values. All data are presented as means ± SEM *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 ****P < 0.0001 vs. control. B Quantification of neuronal soma which show at least one characteristically neuronal calcium event in day 50 control and 1q21.1 deletion culture treated for 10 days with vehicle (DMSO) or verapamil (n ≥ 3/group). C Number of neuronal calcium events recorded per minute in day 50 control and 1q21.1 deletion cultures treated for 10 days with vehicle (DMSO) or verapamil. Both genotype (F1,28 = 71.64; P < 0.0001; n ≥ 3/group) and the addition of verapamil (F2,28 = 79.56; P < 0.0001; n ≥ 3/group) had significant effects on the average rate of calcium events. Furthermore, there was a significant interaction between the effect of genotype and drug (F2,28 = 162.4; P < 0.0001; n ≥ 3/group) on the rate of calcium events. D Example traces of single neurons from both control and 1q21.1 deletion neurons treated with vehicle or verapamil. E Quantification of soma which show at least one characteristically neuronal calcium event in day 50 control and 1q21.1 deletion cultures treated for 10 days with vehicle (DMSO) or roscovitine. Only genotype had a significant effect on the percentage of active cells (F1,22 = 463.9; P < 0.0001; n ≥ 3/group). F Number of characteristically neuronal calcium events recorded per minute in day 50 control and 1q21.1 duplication cultures treated for 10 days with vehicle (DMSO) or roscovitine. Both genotype (F1,22 = 38.1; P < 0.0001; n ≥ 3/group) and the addition of roscovitine (F2,22 = 63.87; P < 0.0001; n ≥ 3/group) had significant effects on the average rate of calcium events. Furthermore, there was a significant interaction between the effect of genotype and drug (F2,22 = 16.06; P < 0.0001; n ≥ 3/group) on the rate of calcium events. G Representative traces of single neurons from both control and 1q21.1 duplication cultures treated with vehicle or roscovitine. Data sets were analysed by two-way ANOVA with post hoc comparisons using Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test comparing to control vehicle treated samples. Stars above points represent Dunnett-corrected post hoc tests. All data are presented as means ± SEM; ***P < 0.001 ****P < 0.0001 vs. vehicle treated control.