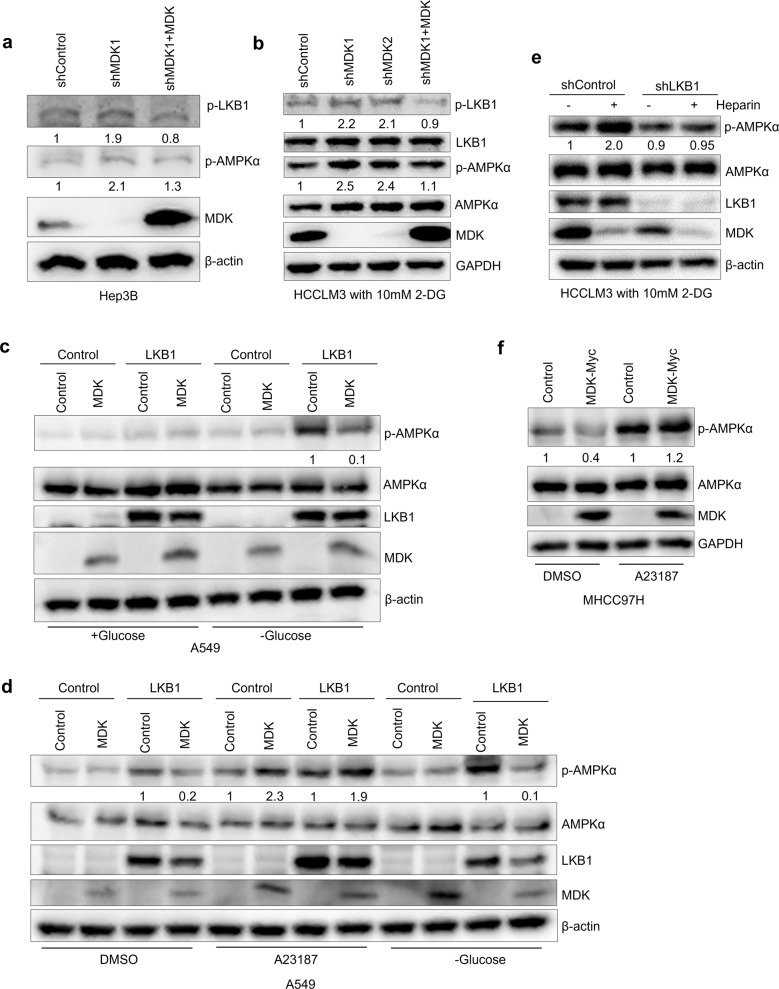
Fig. 3. Midkine suppresses AMPKα activation through LKB1.
a–b Western blot analysis of the Hep3B cells transduced with MDK shRNA1 and restored MDK in the MDK-knockdown cells (a) and the HCCLM3 cells transduced with two independent MDK shRNAs and restored MDK in the MDK-knockdown cells after 4 h of 10 mM 2-DG treatment (b). c–d Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies against p-LKB1, LKB1, p-AMPKα, AMPKα, MDK, and β-actin. Western blot analysis of the A549 cells transduced with LKB1 alone or in combination with MDK and the control cells with glucose starvation for 2 h (c) and the A549 cells transduced with LKB1 alone or in combination with MDK and the control cells with DMSO or A23187 (10 μg/ml) treatment or glucose starvation for 2 h (d). Western blot analysis was performed with antibodies against p-AMPKα, AMPKα, LKB1, MDK, and β-actin. e Western blot analysis of p-AMPKα, AMPKα, LKB1, MDK, and β-actin in the HCCLM3 cells transduced with LKB1 shRNA and the control cells with or without heparin (30 μg/ml) treatment and 10 mM 2-DG treatment for 4 h. f Western blot analysis of p-AMPKα, AMPKα, MDK, and β-actin from the MHCC97H cells transduced with MDK-Myc and the control cells treated with DMSO or A23187 (10 μg/ml).