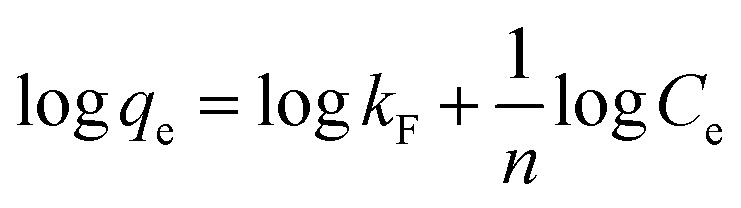| Langmuir |
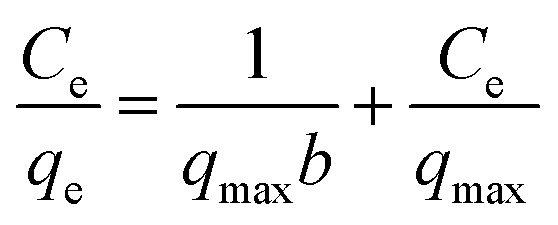 , RL = 1/(1 + bC0), RL > 1 (unfavorable adsorption), RL = 1 (linear adsorption), 0 < RL < 1 (favorable adsorption), RL = 0 (irreversible adsorption) , RL = 1/(1 + bC0), RL > 1 (unfavorable adsorption), RL = 1 (linear adsorption), 0 < RL < 1 (favorable adsorption), RL = 0 (irreversible adsorption) |
C
e (mg L−1): equilibrium concentration of the residual MO in the solution |
56 and 57
|
|
q
e (mg g−1): removed amount of MO at equilibrium |
|
q
max (mg g−1): maximum adsorption capacity |
|
b (L mg−1): Langmuir constant |
|
q
max = 1/slope |
|
b = slope/intercept |
|
C
0: initial MO concentration |
|
R
L: equilibrium parameter of Langmuir equation |
| Freundlich |
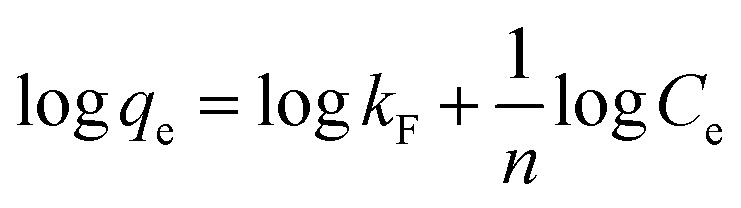
|
C
e (mg L−1): equilibrium concentration of the residual MO in the solution |
58
|
|
q
e (mg g−1): removed amount of MO at equilibrium |
|
K
F (mg g−1): MO adsorption capacity |
|
n: heterogeneity factor |
|
k
F = 10intercept
|
| 1/n = slope |
| Temkin |
qe = B ln A + B ln Ce, B = RT/b |
A (L g−1): Temkin isotherm constant (the equilibrium binding constant corresponding to the maximum binding energy) |
59
|
|
B (J mol−1): Temkin constant related to heat of sorption |
|
b: Temkin isotherm constant |
|
R: the gas constant (8.314 J mol−1 K−1) |
|
T: the absolute temperature at 298 K |
|
A = EXP(intercept/slope)
|
|
b = slope |
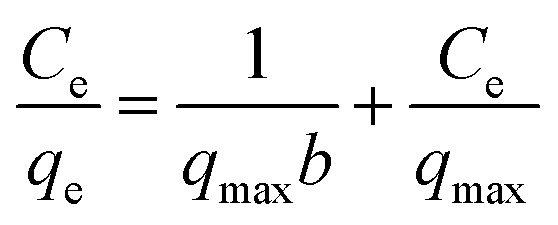 , RL = 1/(1 + bC0), RL > 1 (unfavorable adsorption), RL = 1 (linear adsorption), 0 < RL < 1 (favorable adsorption), RL = 0 (irreversible adsorption)
, RL = 1/(1 + bC0), RL > 1 (unfavorable adsorption), RL = 1 (linear adsorption), 0 < RL < 1 (favorable adsorption), RL = 0 (irreversible adsorption)