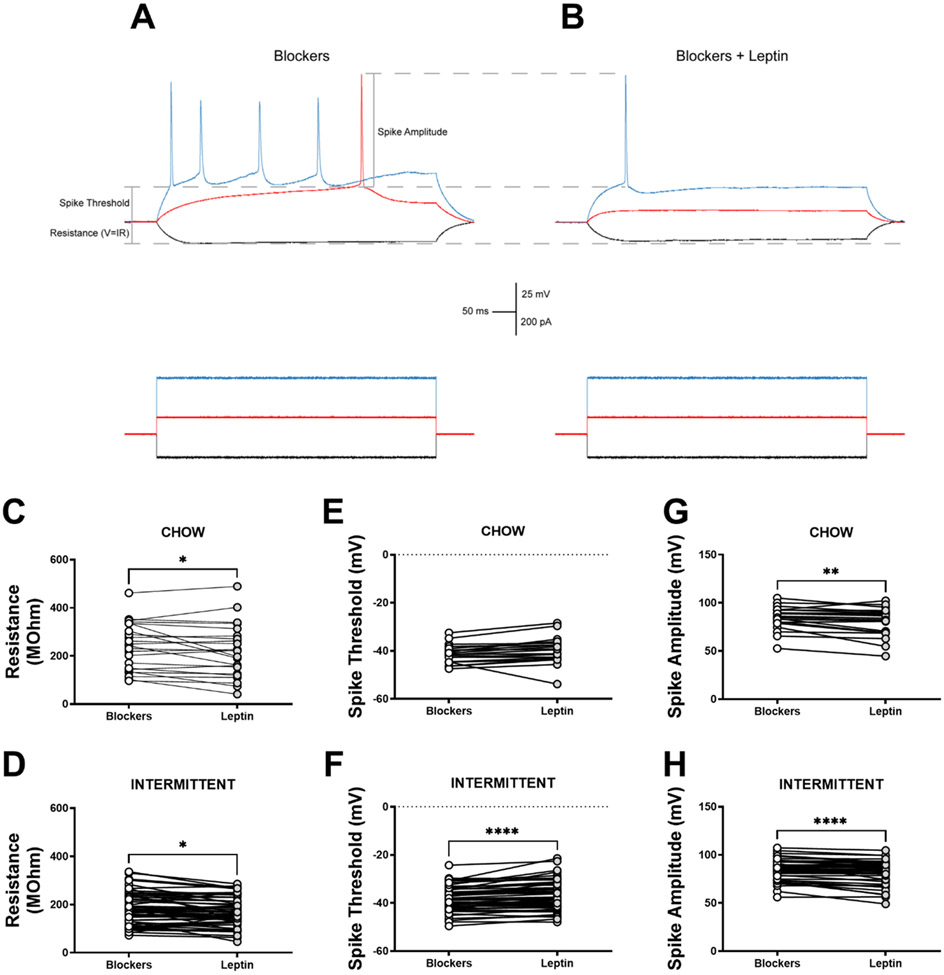
Figure 5: Functional effect of leptin in the anterior insula in rats with intermittent access to a preferred diet.
A) Representative trace of a layer V anterior insula pyramidal neuron showing resistance, AP threshold, and AP amplitude in the presence of GABAB and ionotropic glutamate receptor blockers and depicts how these parameters change in B) the same neuron following superfusion of leptin. Paired comparisons of each recorded cell of ad libitum chow-fed controls and intermittent access rats show a reduction in resistance for both groups (C,D), no effect on threshold for CHOW (E) rats, a significant depolarization in threshold for INT (F) rats, and a significant decrease in amplitude for both CHOW and INT rats (G,H) when leptin is added to the blockers. *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001, ****: p<0.0001, paired comparison Leptin vs Blockers. n=21-57 cells for paired comparison measures.