FIGURE 2.
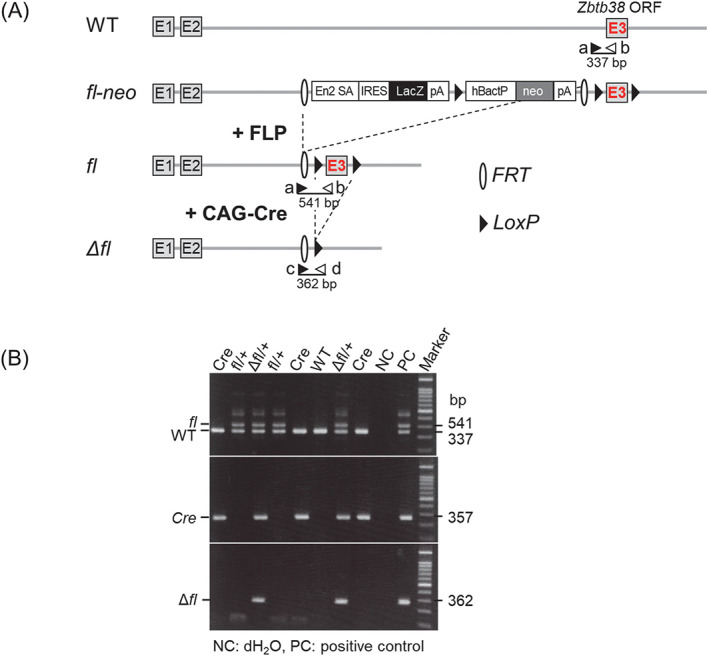
Generation of the Zbtb38 heterozygous KO mice. (A) Schematic diagram of gene targeting strategy. Crossing the fl‐neo allele to a mouse line expressing FLP recombinase removes the lacZ and neo cassettes, resulting in a conditional‐ready allele (fl). When the fl allele is crossed with a mouse strain expressing CAG‐Cre recombinase, exon 3 is deleted, resulting in a null allele (∆fl). Exons are shown as empty boxes and marked by a number inside. LoxP sites (black triangles) and FRT sites (empty semicircles) are shown. En2 SA, mouse En2 splicing acceptor; FLP, flp recombinase; hBactP, human b‐actin promoter; IRES, internal ribosome entry site; neo, neomycin‐resistant gene; pA, poly(A) signal. The position of the primers (a‐d) used for genotyping is shown with arrows, and the expected sizes (bp) of genomic PCR are shown under the individual primer pairs. (B) PCR genotyping of paraffin section of E8.5 embryos isolated from the Zbtb38 fl/+ mice and the CAG‐Cre mice intercrosses. Representative PCR genotyping with primers a ~ d, WT, fl and ∆fl alleles produced a 337‐bp, 541‐bp and 362‐bp bands, respectively. Cre genotyping primer produces a 357 bp band
