Figure 3.
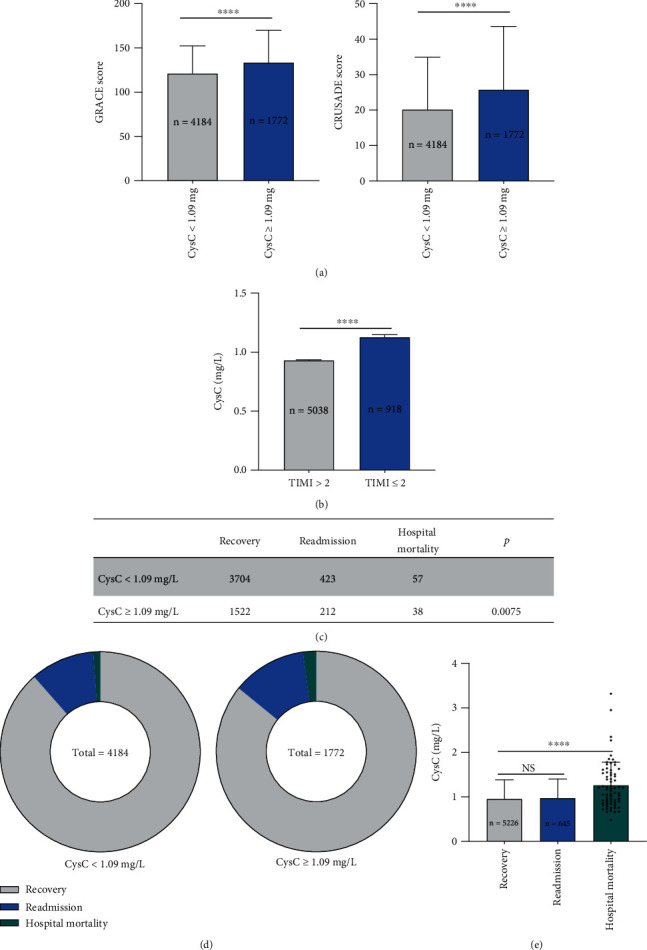
Increased hospital mortality in high-admission CysC cohort with AMI. (a) GRACE and CRUSADE score were significantly higher in high-admission CysC cohort (CysC ≥ 1.09 mg/L) than controls (CysC < 1.09 mg/L). (b) CysC was significantly higher in group TIMI ≤ 2 compared to group TIMI > 2. (c, d) High-admission CysC cohort (CysC ≥ 1.09 mg/L) showed elevated mortality rate even during hospitalization and readmission rate than controls (CysC < 1.09 mg/L). Within the high CysC cohort, 38 (2.14%) patients died for all causes during hospitalization and 212 (11.96%) for readmission. Within the low CysC cohort, 57 (1.36%) patients died for all causes during hospitalization and 423 (10.11%) for readmission. For statistical analysis, χ2 test was performed. (e) AMI patients who died during hospitalization exhibited raised admission CysC value than recovery patients, but no significant difference between readmission and recovery patients. Data were shown in mean ± SD (a, e), mean ± SEM (Bb), or as each individual dot. For statistical analysis, one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak's multiple comparison test was applied, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
