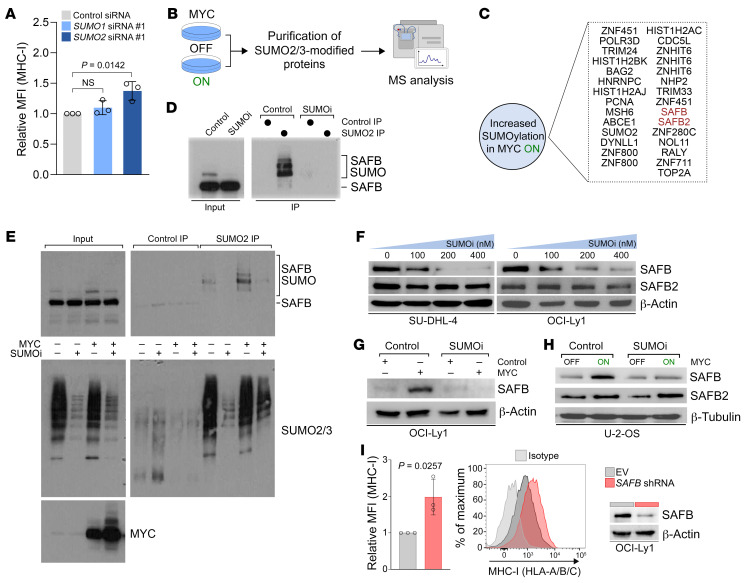
Figure 6. MYC-induced SUMOylation of SAFB suppresses the MHC-I/APM pathway.
(A) MHC-I expression of U-2-OS cells after transfection with specific SUMO1, SUMO2, or control siRNAs (72 h, n = 3). Data represent the mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined by ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. (B) Outline of the experimental setup for the identification of MYC-induced differentially SUMOylated proteins. SUMO2/3-modified proteins were purified from U-2-OS cells after MYC induction for 48 hours and analyzed by MS. (C) Schematic illustration summarizing the results of quantitative MS analysis from U-2-OS cells after MYC induction for 48 hours. The experiment was performed in triplicate. (D) Immunoblot analysis of U-2-OS cells treated with 100 nM SUMOi or control for 72 hours and IP with either SUMO2 or a control antibody. (E) Immunoblot analysis of U-2-OS cells treated with 100 nM SUMOi or control for 72 hours after 48 hours of MYC induction and IP with either SUMO2 or control antibody. (F) Immunoblot analysis of SU-DHL-4 and OCI-Ly1 cells treated with the indicated concentrations of SUMOi (0, 100, 200, 400 nM) or control for 72 hours. (G) Immunoblot analysis of OCI-Ly1 cells transduced with an MYC expression plasmid or a control plasmid. The cells were treated with either 100 nM SUMOi or control for 72 hours. (H) Immunoblot analysis of U-2-OS cells after 48 hours of MYC induction, treated with either 100 nM SUMOi or control for 72 hours. (I) MHC-I expression of OCI-Ly1 cells after transduction with a specific SAFB shRNA or a control vector (n = 3). Data represent the mean ± SD. P value was determined by unpaired t test. Immunoblot analysis of the respective OCI-Ly1 cells.