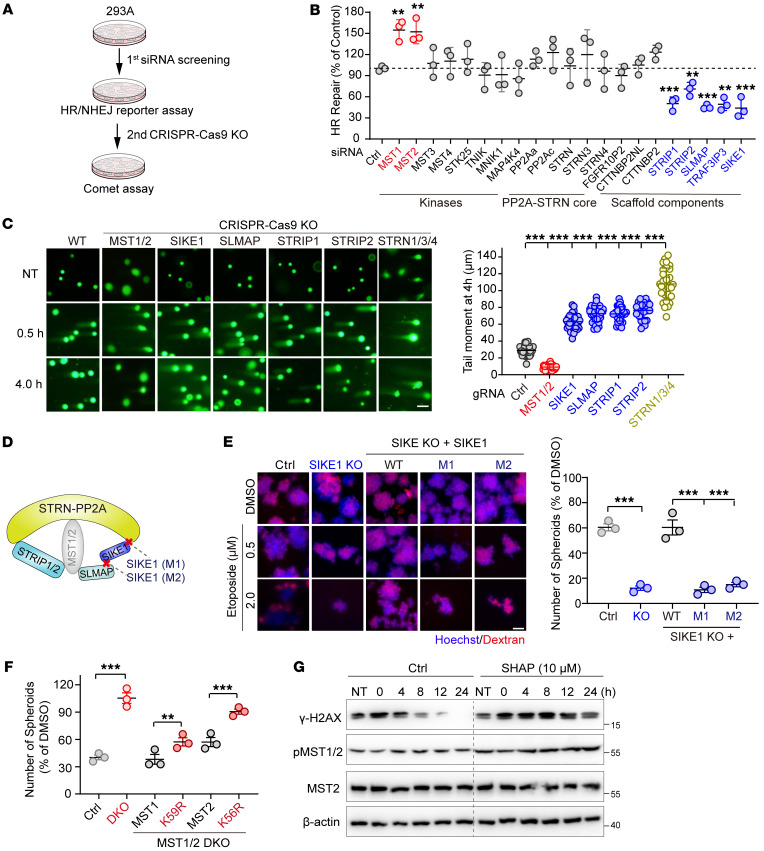
Figure 1. The Hippo-containing STRIPAK complex is essential for DSB repair.
(A) Schematic illustration of the miniscreen of STRIPAK in DSB repair. (B) Plot showing the regulation of HR repair by the siRNA-mediated knockdown components of STRIPAK (n = 3). (C) Images showing the results of the indicated HGC-27 cells exposed to IR (10 Gy) and collected 0.5 and 4 hours after treatment before being subjected to a neutral comet assay (scale bar: 50 μm), and a plot providing quantifications of the tail moment at 4 hours (n = 30 cells/group). (D) Schematic presentation of the assembly of the STRIPAK-MST1/2 complex and SIKE1 mutants (M1 and M2). (E) Images and plot showing that SIKE1 promoted genomic stability within STRIPAK. HGC-27 cells (WT and its derivatives) were first treated with etoposide for 1 hour before being subjected to the sphere formation assay. Scale bar: 60 μm. (F) Plot showing that MST1/2 limited cancer cell sphere formation in a manner dependent on their kinase activity of MST1/2. HGC-27 cells (WT and its derivatives) were treated and processed as in E. (G) Gels showing that SHAP treatment attenuated DNA repair capacity. HGC-27 cells pretreated with etoposide for 1 hour were further incubated with or without SHAP peptides. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, by 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, compared with control (B and C) and unpaired Student t test (E and F). See also Supplemental Figures 1 and 2. Ctrl, control.