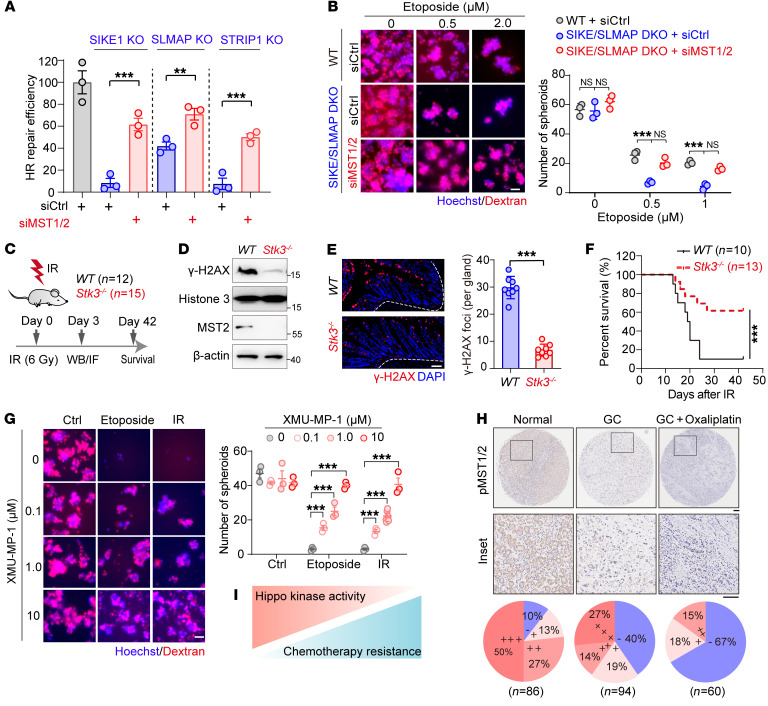
Figure 7. Loss of Hippo kinase activity endows cancer cells with resistance to radio- and chemotherapy.
(A) Plot showing that MST1/2 ablation restored HR repair in STRIPAK component–deficient cells. 293A cells (WT or KOs) were transfected with the indicated siRNAs before being subjected to an HR reporter assay (n = 3). (B) Images of samples from HGC-27 cells (WT and SIKE1/SLMAP-DKO) transfected with the indicated siRNAs and then subjected to a sphere formation assay (n = 3). Scale bar: 60 μm. (C–F) Results showing that MST2 deficiency induced radioresistance in vivo. (C) WT and Stk3–/– mice were exposed to 6 Gy whole-body IR. Residual DNA damage in intestinal tissues was examined at 3 days via both (D) Western blotting and (E) immunofluorescence analysis using anti–γ-H2AX antibody, and (F) overall survival was assessed until 6 weeks after IR. Representative images in intestinal tissues were quantified and analyzed (n = 8 glands from 2 mice in each group). Scale bar: 10 μm. (G) Images showing that MST1/2 inactivation promoted cancer cell resistance to etoposide. HGC-27 cells were treated with etoposide with or without XMU–MP-1 and analyzed using the sphere formation assay (n = 3). Scale bar: 60 μm. (H) Reduced MST1/2 kinase activity in tumor tissues after chemotherapy. IHC analysis of p-MST1/2 staining of tissues derived from adjacent normal tissue, GC tumors, and GC tumors after oxaliplatin treatment. Scale bar:100 μm, the enlarged inserts were magnified 5 times form original images. (I) Schematic illustration of the negative correlation between Hippo kinase activity and acquired drug resistance. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, by unpaired Student’s t test (A and E) and 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test (B and G). The survival analysis was performed using the log-rank test (F). See also Supplemental Figure 8.