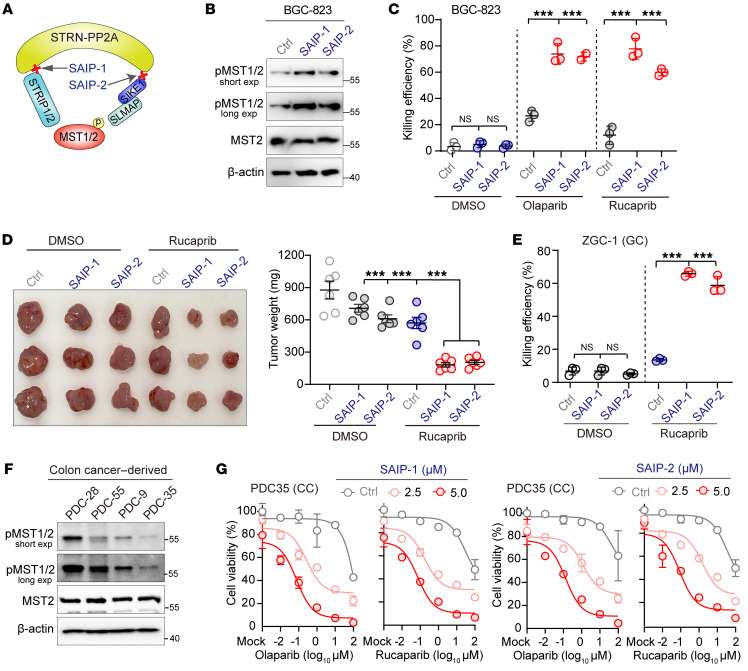
Figure 9. Cotargeting of STRIPAK and PARP elicits synthetic lethality in tumor cells.
(A) Schematic illustration of the STRIPAK assembly peptide inhibitors SAIP-1 and SAIP-2. (B) Gels showing that inclusion of SAIP-1 and SAIP-2 each restored Hippo kinase activity in BGC-823 cells. (C) Plots showing that SAIP1/2 in combination with PARPi resulted in synthetic lethality in BGC-823 cancer cells (n = 3). (D) Photograph showing that SAIP-1/2 synergistically augmented rucaparib-mediated antitumor efficiency in vivo (n = 3 mice/group in 1 experiment; n = 2 assays). Dot plot represents mouse tumor weights from 2 experiments (n = 6 mice per group) in each group. (E) Plots showing that SAIP-1/2 had a synthetic lethality effect with PARPi in gastric PDCs with low Hippo activity (n = 3). (F and G) Gels and plots showing that SAIP-1/2 had a synthetic lethality effect with PARPi in colon PDCs with low Hippo activity. (F) Western blot analysis of p-MST1/2 levels in 4 colon cancer PDC lines. (G) PDC35 cells were further treated with various doses of olaparib or rucaparib in the presence of 0, 2.5, and 5.0 μM SAIP-1 (left panel) or SAIP-2 (right panel) for 24 hours before cell viability analysis. CC, colon cancer. ***P < 0.001, by 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test (C, D, and E). See also Supplemental Figure 10.