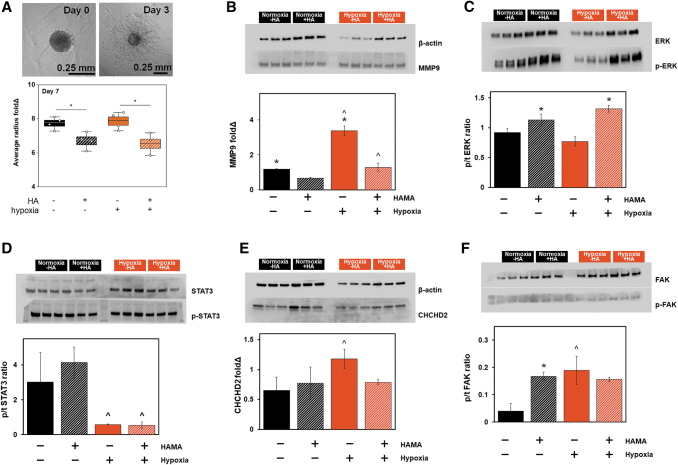
FIG. 2.
Profiling shifts in GBM6 invasion and signal transduction in response to extracellular hypoxia and matrix-bound HA. (A) Representative image of GelMA-only GBM6 invasion from day 0 to 3 visualized by spheroid invasion assay and the quantitative radius fold change results on day 7. (B–E) Proteomic activity quantified by Western blotting (n = 3; *p < 0.05 for −/+ HAMA; ^p < 0.05 for −/+ hypoxia). (B) Hypoxia increased MMP9 activity regardless of the presence or absence of matrix-bound HA. (C) ERK1/2 phosphorylation increased in response to matrix-bound HA, but not in response to hypoxic culture. (D) STAT3 phosphorylation significantly reduced in response to hypoxia. (E) CHCHD2 was elevated in hypoxia in the absence of matrix-bound HA. (F) FAK phosphorylation was increased in response to matrix-immobilized HA, hypoxia, and the combination of the two, although the effects were not additive or synergistic. ^p < 0.05 for +/− hypoxia; *p < 0.05 for +/− HAMA. CHCHD2, coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containing 2; ERK, extracellular regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; MMP9, matrix metalloproteinase 9; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Color images are available online.