Figure1. Potential mechanisms underlying the effects of naringin and naringenin on lipid metabolism.
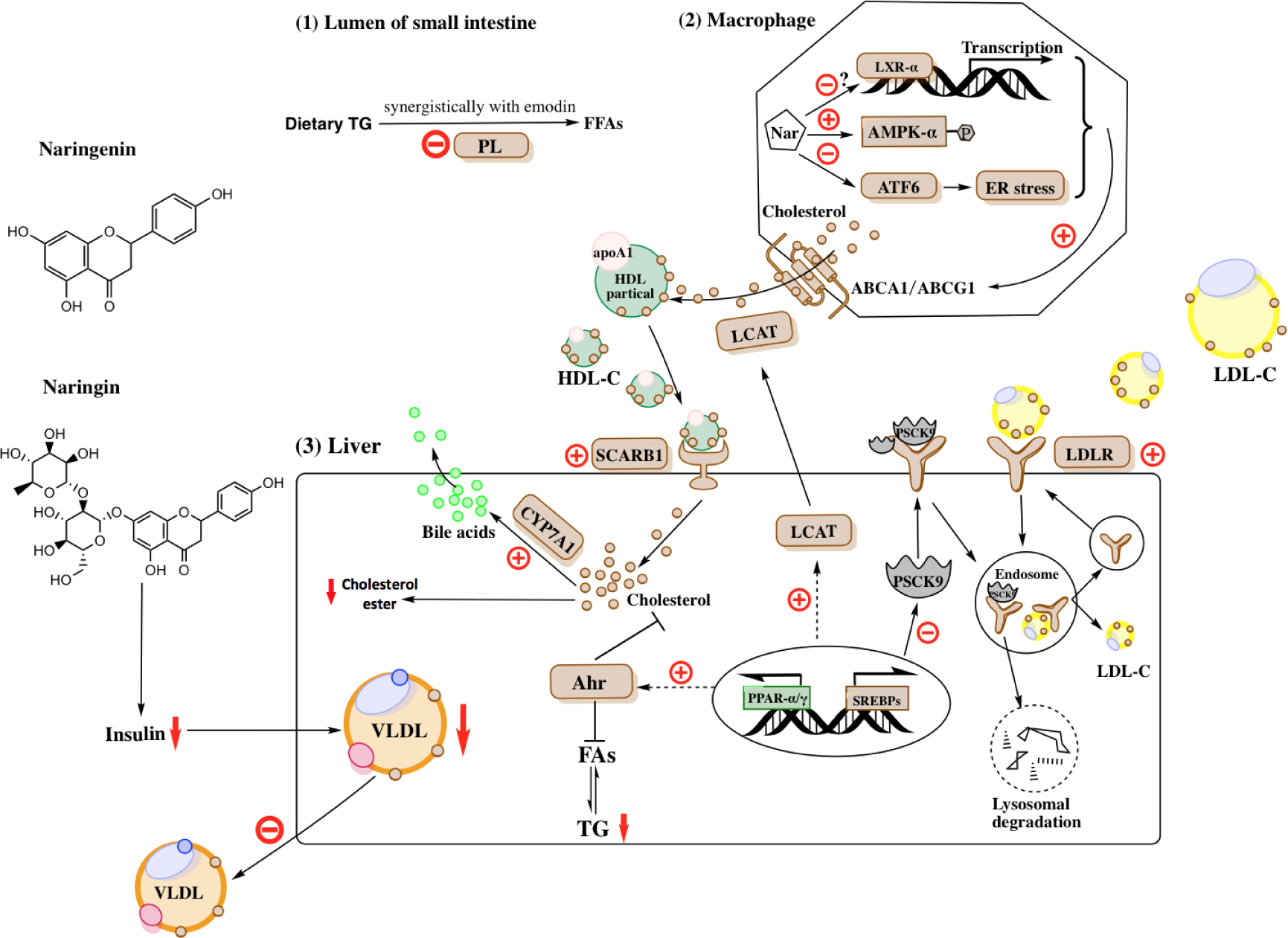
Naringin and naringenin have been shown lipid-lowering effects in various animal models and human trials. Recent studies have revealed novel mechanisms of naringin and naringenin on lipid metabolism (1) Naringin synergistically inhibits PL activity with emodin to decrease dietary fat absorption in the small intestine; (2) Naringin and naringenin increase reverse cholesterol transport by up-regulating ABCA1/ABCG1, SCARB1, and LCAT expression in macrophages and hepatocytes. The up-regulation of ABCA1/ABCG1 in macrophages is likely mediated through ER stress-ATF6 pathway, AMPK pathway, and LXR-α activation; (3) Naringin and naringenin up-regulate hepatic LDLR by suppressing PSCK9, which contributes to LDL-C clearance from circulation. In addition, naringin and naringenin decrease hepatic cholesterol ester content by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis through up-regulating Ahr expression and increasing cholesterol clearance through CYP7A1, which converts cholesterol to bile acids. Moreover, up-regulated Ahr expression contributes to decreased hepatic TG level by inhibiting FA synthesis. Further, naringenin and naringenin may decrease VLDL production through improving hepatic insulin sensitivity.
PL, pancreatic lipase; HDL, High-density lipoprotein; ApoA1, apolipoprotein A1; HDL-C, High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Nar, naringin/naringenin; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette subfamily A member1; ABCG1, ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member1; SCARB1, Scavenger receptor class B type 1; LCAT, lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; LXR, Liver X receptor; LDL-C, Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDLR, Low-density lipoprotein receptor; PSCK9, Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; Ahr, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; CYP7A1, cytochrome P450 family 7 subfamily A member 1; FAs, fatty acids; TG, triglyceride; PPAR, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; SREBPs, Sterol regulatory element-binding protein.
