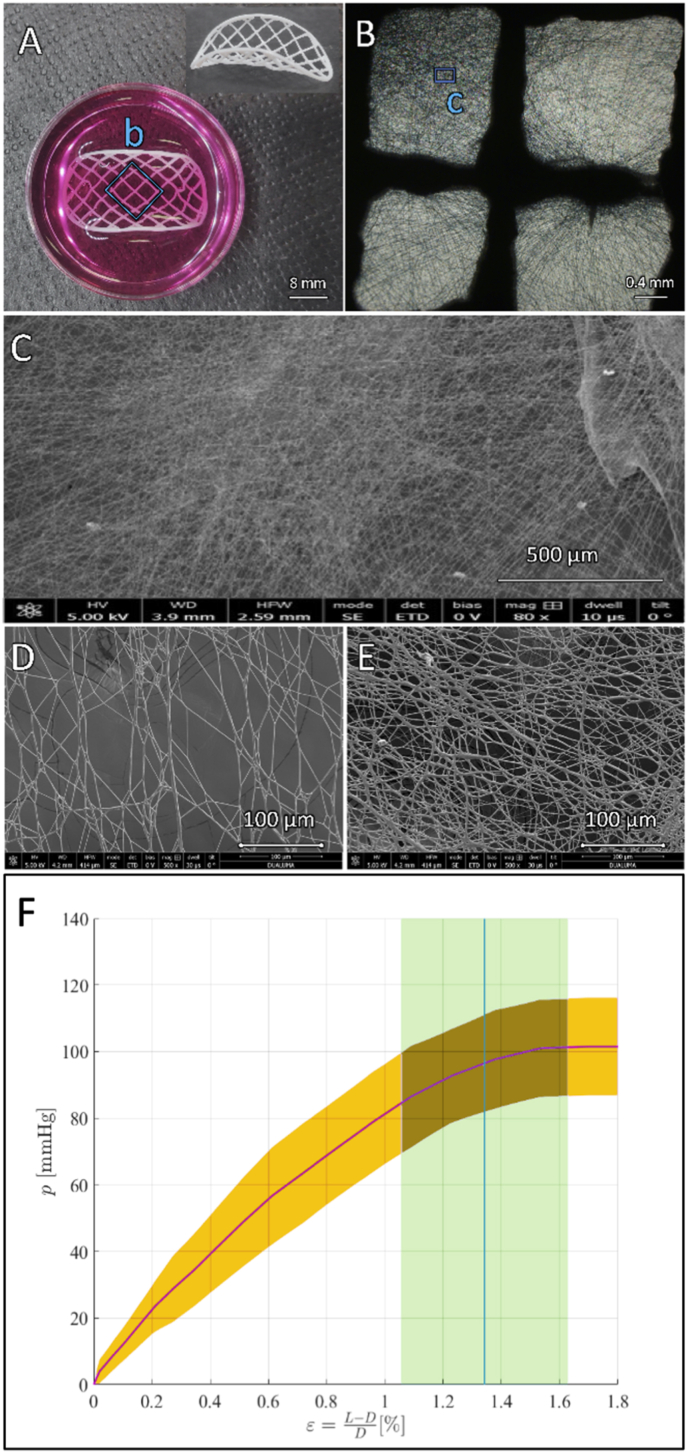
Fig. 3.
3D print of vascular scaffold and 3D print of vascular scaffold and pressure-strain implant curve. A. Macroscopic patch view. The three-dimensional patch geometry and the gross strands printed with fused deposition modelling can be seen. B. Microscopic optic view of the grids allows visualization of the nanofibers created with electrospinning. C. Electronic microscopy view demonstrating the spatial arrangement and thickness of the nanofibers below 1 μm. D. Upper surface, low density area demonstrating larger pore diameter. E. Lower surface, high density area. F. Pressure (p, mmHg), strain (ε, %).