Figure 4. Pathobiologic Contributors to Pulmonary Hypertension in Left Heart Disease.
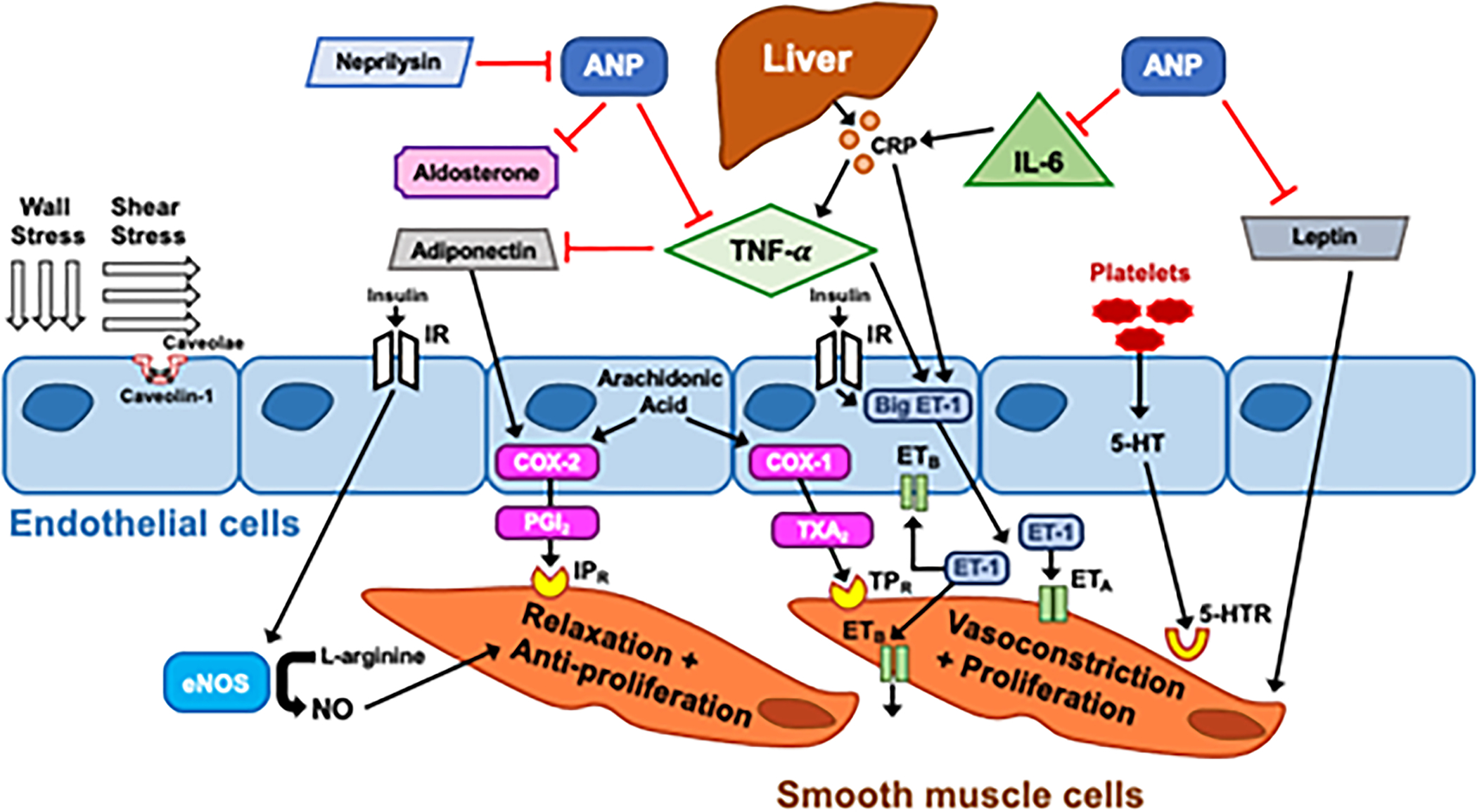
Wall stress and shear stress are drivers of adaptive and maladaptive processes resulting in endothelial dysfunction, smooth muscle hypertrophy, and inflammation. Many of these mediators of endothelial function in PH-LHD that have effects both systemically and locally. eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase, IR:insulin receptor, NO: nitric oxide, ANP: atrial natriuretic peptide, TNF-α:Tumor necrosis factor alpha, COX: cyclooxygenase, PGI2:Prostaglandin I2, IPR: Prostacyclin I2 receptor, TXA2: thromboxane A2, TPR: Thromboxane A2 receptor, ET-1: endothelin-1, ETA: Endothelin receptor A, 5-HT: serotonin, 5-HTR: serotonin receptor, IL-6: Interleukin-6, CRP: C-reactive protein
