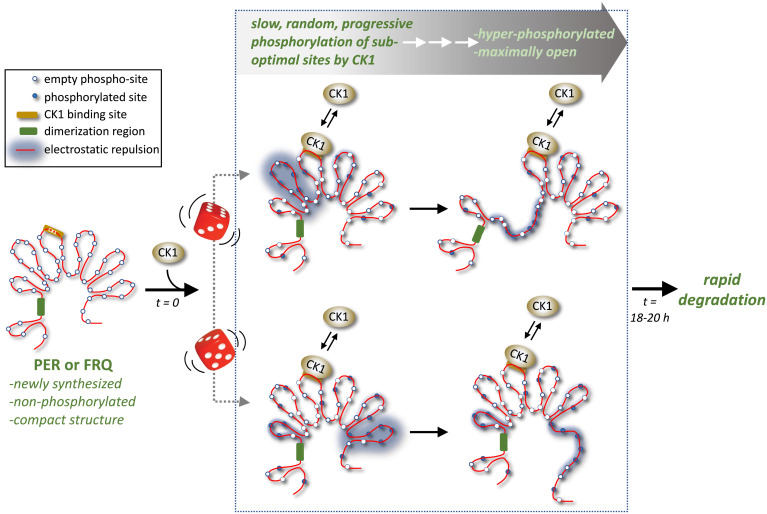
Fig. 1.
Casein kinase 1 works with functionally similar modules on PER and FRQ to drive their slow conversion from compact nonphosphorylated forms to extended hyperphosphorylated forms over a daily time scale, despite randomness in pathways to hyperphosphorylation (the beginnings of two random paths are indicated by the dice). Conserved modules include long stretches of highly disordered regions attached to a centrally located CK1 binding site. Increased phosphorylation by CK1 leads to electrostatic repulsion that force more open conformations, eventually facilitating the rapid degradation of PER and FRQ, which helps set the daily timing for the next round of PER and FRQ synthesis (not shown). Adapted from ref. 7.