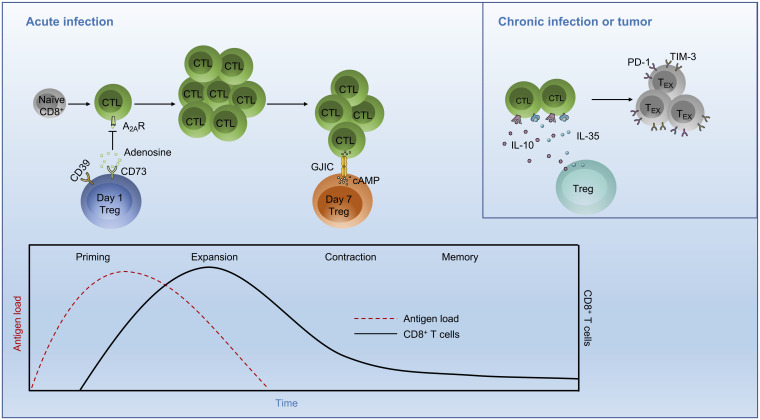
Fig. 1.
Temporal effects of Treg cells on CD8+ T cell responses in infection. During the priming phase of an acute infection, the first wave of Treg cell expansion occurs at day 1 postinfection. These Treg cells are capable of cell contact-independent suppressive function mediated by rapid generation of adenosine, which inhibits A2AR-expressing CD8+ T cell function. A second wave of Treg cell expansion occurs at day 7 postinfection, associated with the stage of peak CTL expansion. This Treg cell population is distinct from cells arising on day 1 postinfection and suppresses CTL proliferation by cell contact-dependent transfer of cAMP to CTLs via GJIC. (Inset) In a chronic infection or tumor, the immunosuppressive cytokines IL-10 and IL-35 are secreted by Treg cells and promote CD8+ T cell exhaustion, which is a progressive process characterized by loss of effector function and up-regulation of inhibitory receptors, such as PD-1 and TIM-3. A2AR, adenosine A2A receptor; GJIC, gap junction intracellular communication; TEX, exhausted T cells.