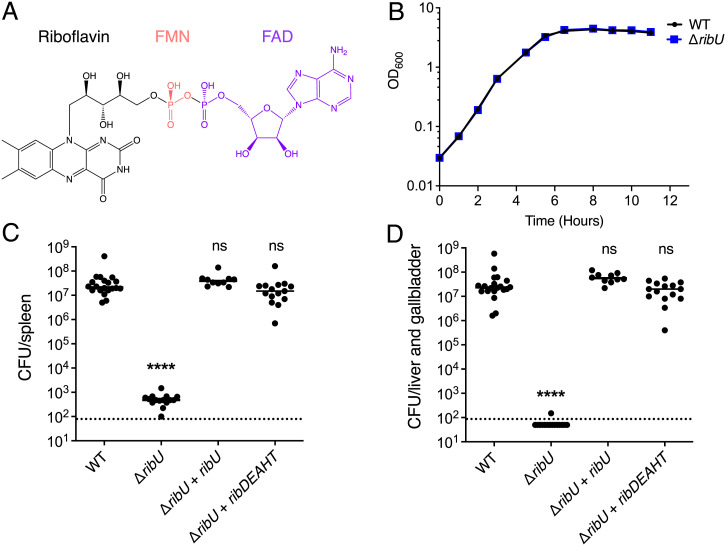
Fig. 1.
RibU is essential for virulence but dispensable for growth in nutrient-rich media. (A) Structures of riboflavin (black), FMN (red), and FAD (purple). Riboflavin is phosphorylated by riboflavin kinases to produce FMN. FAD synthetases adenylylate FMN to generate FAD. (B) Broth growth curves of L. monocytogenes strains grown in nutrient-rich media. OD600 was used to determine cell density. The means and SDs of three independent experiments are shown. Note: both the WT and ΔribU mutant growth curves are superimposable. (C and D) Bacterial burdens in CD-1 mice infected intravenously with 1 × 105 CFUs of indicated L. monocytogenes strains. At 48 h postinfection, the spleens (C) and livers (D) were harvested, homogenized, and plated to determine the CFUs per organ. The data show the combination of at least two independent experiments: WT and ΔribU (n = 20 mice), ΔribU + ribDEAHT (n = 15 mice), and ΔribU + ribU (n = 10 mice). The black lines represent the median CFUs for each strain. The dashed line represents the limit of detection. Statistical significance of logarithmically transformed CFU values was determined using one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s posttest using WT as the control. ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant, P > 0.05.