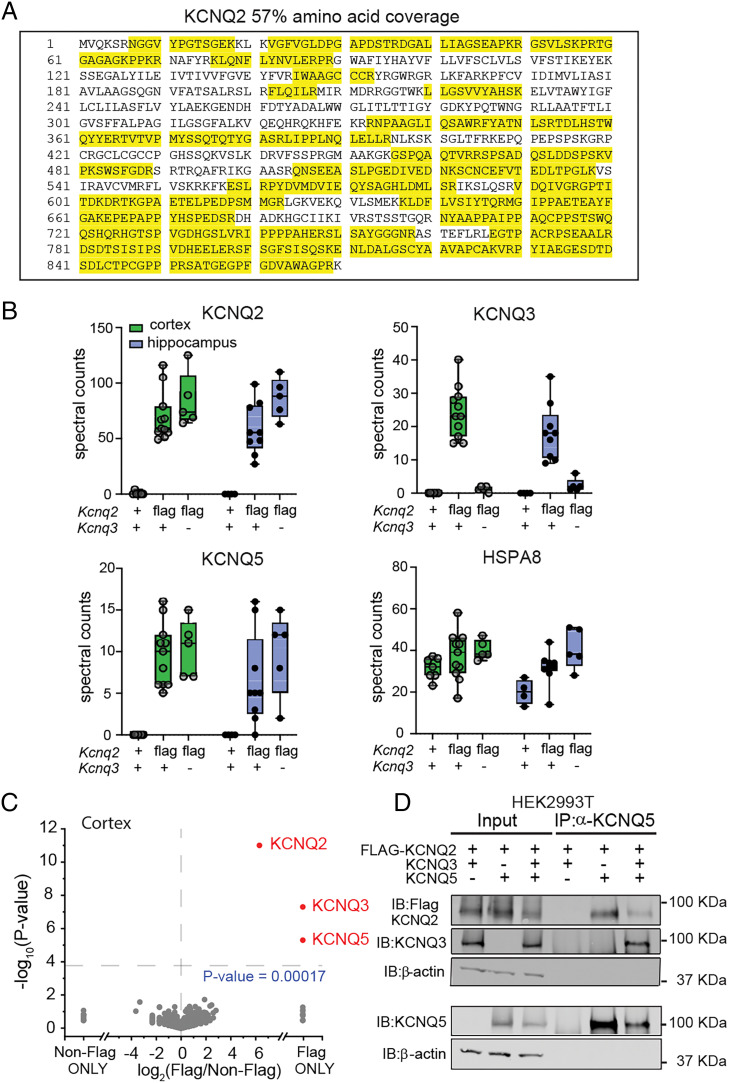
Fig. 4.
KCNQ2 and KCNQ5 form a complex in the brain. (A) Representative sequence coverage of KCNQ2 channels from anti-FLAG (M2 antibody) immunoprecipitated proteins followed by mass spectrometry analysis. Yellow indicates recovered peptides. (B) Total nonnormalized spectral counts of KCNQ2, KCNQ3, and KCNQ5 channels identified in Kcnq2+/+;Kcnq3+/+ (cortex, n = 7; hippocampus, n = 4), Kcnq2flag/flagKcnq3+/+ (cortex, n = 11; hippocampus, n = 8), and Kcnq2flag/flag;Kcnq3−/− (cortex, n = 5; hippocampus, n = 5). Data are displayed as box and whisker plots. (C) Volcano plot comparing calculated log2 fold change using unnormalized spectral count values of different cortical proteins identified in Kcnq2+/+;Kcnq3+/+ (n = 7) and Kcnq2flag/flag;Kcnq3+/+ (n = 7) mice. (D) Immunoblot showing immunoprecipitated proteins from HEK293T cells expressing various 3XFLAG-KCNQ2, KCNQ3, and KCNQ5 channel combinations. Immunoprecipitation was performed using an anti-KCNQ5 antibody. n indicates number of mice.