FIGURE 1.
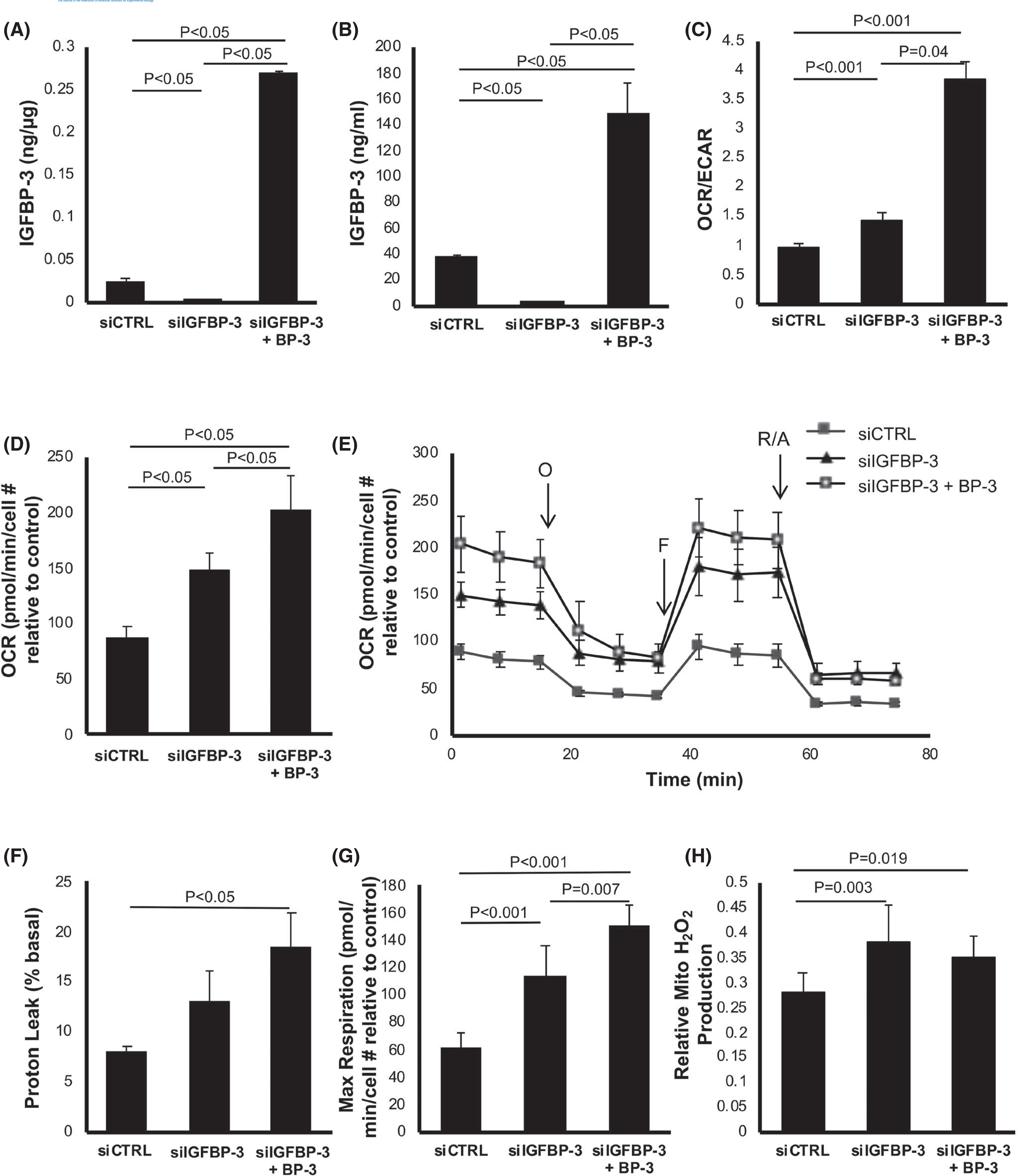
IGFBP-3 regulates mitochondrial respiration in corneal epithelial cells. hTCEpi cells were transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting IGFBP-3. Non-targeting oligonucleotides were used as a control. Cells were cultured in KBM with or without 500 ng/ml rhIGFBP-3 for 24 h. Knockdown efficiency was confirmed using ELISA. (A) Intracellular IGFBP-3 expression was significantly decreased following knockdown (p < .05). Co-treatment with rhIGFBP-3 increased intracellular levels compared to the knockdown and siRNA control (p < .05). (B) Extracellular IGFBP-3 was similarly decreased after knockdown (p < .05) and increased after the addition of rhIGFBP-3 (p < .05). (C–H) Seahorse metabolic flux analysis. (C) The OCR/ECAR ratio was increased following knockdown of IGFBP-3 (p < .001). Co-treatment with rhIGFBP-3 further increased the OCR/ECAR ratio compared to the control (p < .001) and knockdown (p = .04). (D) OCR was increased in IGFBP-3 knockdown cells (p < .05) and further increased when treated with rhIGFBP-3 (p < .05). (E) OCR plotted as a function of time. Time points for the addition of oligomycin (O), FCCP (F), and rotenone/antimycin A (R/A) are indicated. (F) The proton leak was not increased following IGFBP-3 knockdown, but was increased by the addition of rhIGFBP-3 (p < .05). (G) In contrast, maximal respiration showed the same sequential increases as those seen with OCR in both knockdown and rhIGFBP-3-treated cells (p < .001 and p = .007, respectively). (H) Mitochondrial H2O2 concentrations were measured using an Amplex Red florescence assay. Knockdown of IGFBP-3 increased ROS levels compared to control (p = .003). Co-treatment with rhIGFBP-3 did not further increase ROS levels compared to the knockdown, but ROS levels were increased compared to control (p = .019). Data expressed as mean ± standard deviation from one representative experiment, N = 3. One-way ANOVA with Student–Newman–Keuls post hoc multiple comparison test. ECAR, extracellular acidification rate; KBM, keratinocyte basal media; OCR, oxygen consumption rate
