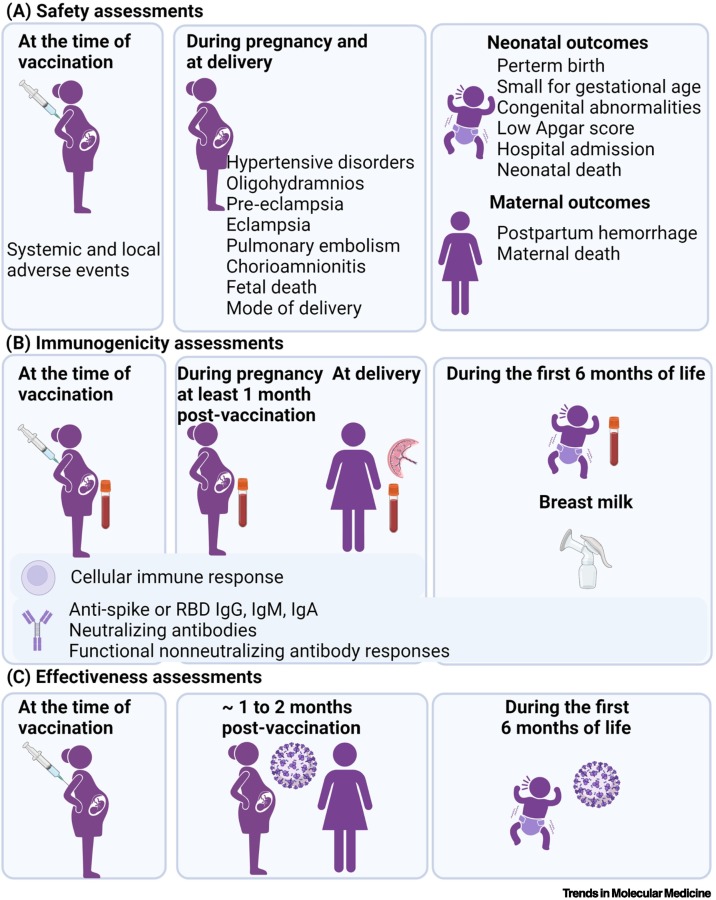
Figure 1.
Different approaches used to determine COVID-19 vaccine safety, immunogenicity, and effectiveness in pregnant women.
(A) The safety of COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant women has been described for systemic and local adverse events, and for pregnancy, maternal, and neonatal outcomes. (B) Anti-SARS-CoV-2 binding (IgG, IgM) and neutralizing antibodies have been quantified in maternal and cord blood samples. Functional non-neutralizing antibody responses were assessed by systems serology approaches in maternal and cord blood samples. IgG, IgM, IgA have also been measured in breastmilk and IgG in infants up to 6 months of age. Cellular immune responses have been described in pregnant women. (C) The effectiveness of maternal COVID-19 vaccination against documented infection of the women during the 2 months after vaccination, and in their infants <6 months of age against COVID-19-associated hospitalization. Figure created with biorender.com.