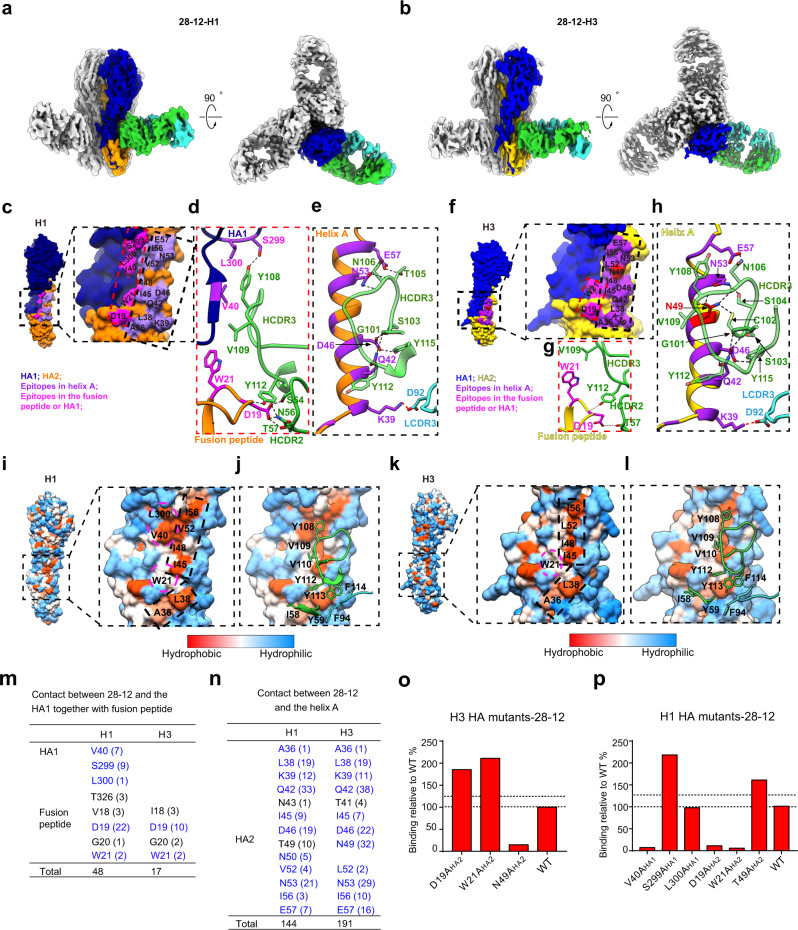
Fig. 4. Cryo-EM structures of 28-12-H3 and 28-12-H1 and distinct recognition patterns of 28-12 Fab to H3 and H1 HAs.
a, b Cryo-EM maps of the 28-12-H1 (a) and 28-12-H3 (b) complexes. One HA protomer and the cognate 28-12 Fab fragment are highlighted in color, and the other two copies in the trimer are colored gray. H1 HA1/HA2 and H3 HA1/HA2 are colored in navy blue, orange, blue, and gold, respectively. The heavy and light chains of 28-12 Fab are colored in lime green and turquoise, respectively. This color scheme was followed throughout. c, f Epitopes of the 28-12 Fab on H1 (c) and H3 (f), respectively. The epitopes in helix A (indicated by black dashed box) and fusion peptide/HA1 (indicated by red dashed box) are colored in purple and magenta, respectively. H3 residue N49HA2 is specifically showed in red. d, g Hydrogen bonds between 28-12 Fab and the fusion peptide/HA1 of H1 (d) or H3 (g). e, h Hydrogen bonds formed between helix A of H1 (e) or H3 (h) and 28-12 Fab. The salt bridge and hydrogen bond are shown as red and black dashed lines, respectively. i, k Hydrophobic epitopes in the H1 (i) and H3 (k) HAs. The hydrophobic epitopes are classified into two parts, helix A in the dashed black box and the fusion peptide and HA1 residues in the dashed magenta circle. j, l The Fab residues involved in hydrophobic contacts with H1 (j) and H3 (l) are shown with side chains. m The number of atom-to-atom contacts between 28-12 Fab and the fusion peptide/HA1 residues. n The number of atom-to-atom contacts between 28-12 Fab and the helix A. The epitopes involved in the hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen bond, and salt bridge are colored in blue. o, p 28-12 binding to H1 and H3 HA mutants with alanine substitutions. Each value is calculated as the binding ratio relative to that of the WT HA (%). The two black dotted lines represent 100 and 125% relative binding to the WT data, respectively. The mean values of duplicates are shown from two independent experiments (o, p).