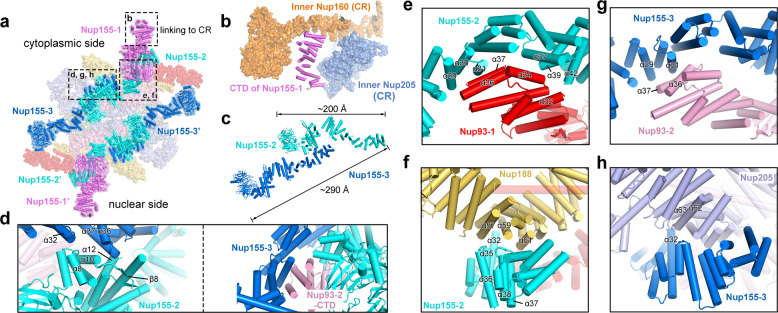
Fig. 5. Nup155 links the central scaffold.
a An overall view of six Nup155 molecules in each IR subunit. Of the six Nup155 molecules, Nup155-2 and Nup155-3 form a dimer on the cytoplasmic side; Nup155-2′ and Nup155-3′ form a homo-dimer on the nuclear side. b Nup155 connects the IR subunit to the CR subunit. The C-terminal helices of Nup155 on the cytoplasmic side of the IR subunit are sandwiched by inner Nup160 and inner Nup205 of the CR subunit. c A close-up view on the Nup155 homo-dimer. The helical domains of Nup155-2 and Nup155-3 interact with each other in a head-to-tail fashion, generating an elongated Nup155 homo-dimer of ~290 Å in length. d Close-up views on the interface between Nup155-2 and Nup155-3. Two views are shown. e A close-up view on the interface between Nup155-2 and Nup93-1. f A close-up view on the interface between Nup155-2 and Nup188. g A close-up view on the interface between Nup155-3 and Nup93-2. This interface is analogous to that between Nup155-2 and Nup93-1. h A close-up view on the interface between Nup155-3 and Nup205. This interface is analogous to that between Nup155-2 and Nup188.