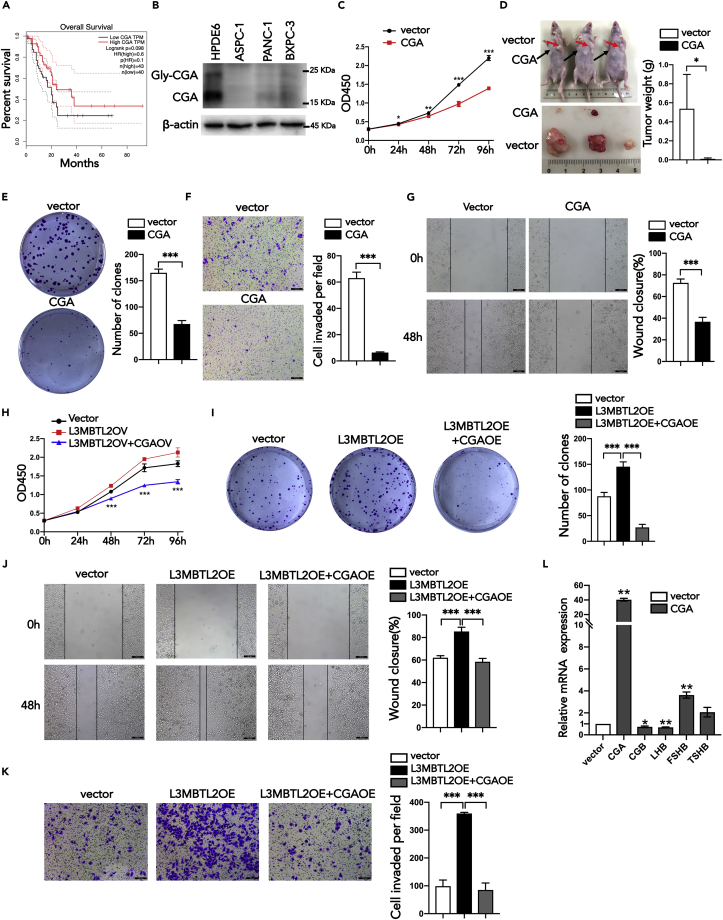
Figure 5.
CGA inhibits pancreatic cancer progression
(A) The correlations between the expression of CGA and patient survival rate.
(B) The protein levels of CGA in pancreatic cancer cells and pancreatic ductal epithelial cells.
(C) Cell proliferation of PANC-1 cells expressing exogenous CGA.
(D) The volumes and weight of subcutaneous tumors formed by PANC-1 cells expressing exogenous CGA and vectors.
(E) Clone forming assay of CGA-overexpressing PANC-1 cells.
(F and G) Transwell assays (F) and wound healing assays (G) of PANC-1 cells expressing exogenous CGA and vectors.
(H–K) CGA overexpression abolished the promotion of cell proliferation (H), colony formation capacity (I), migration (J) and invasion (K) caused by overexpression of L3MBTL2 in PANC-1 cells.
(L) The relative mRNA levels of CGA, CGB, LHB, FSHB, and TSHB in CGA-overexpressing PANC-1 cells. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, t-tests. Scale bars, 100 μm (F, G, J and K).