Figure 2: Expression of Anopheles stephensi odd-paired and ftz transcription factor-1 occur in an anterior to posterior wave.
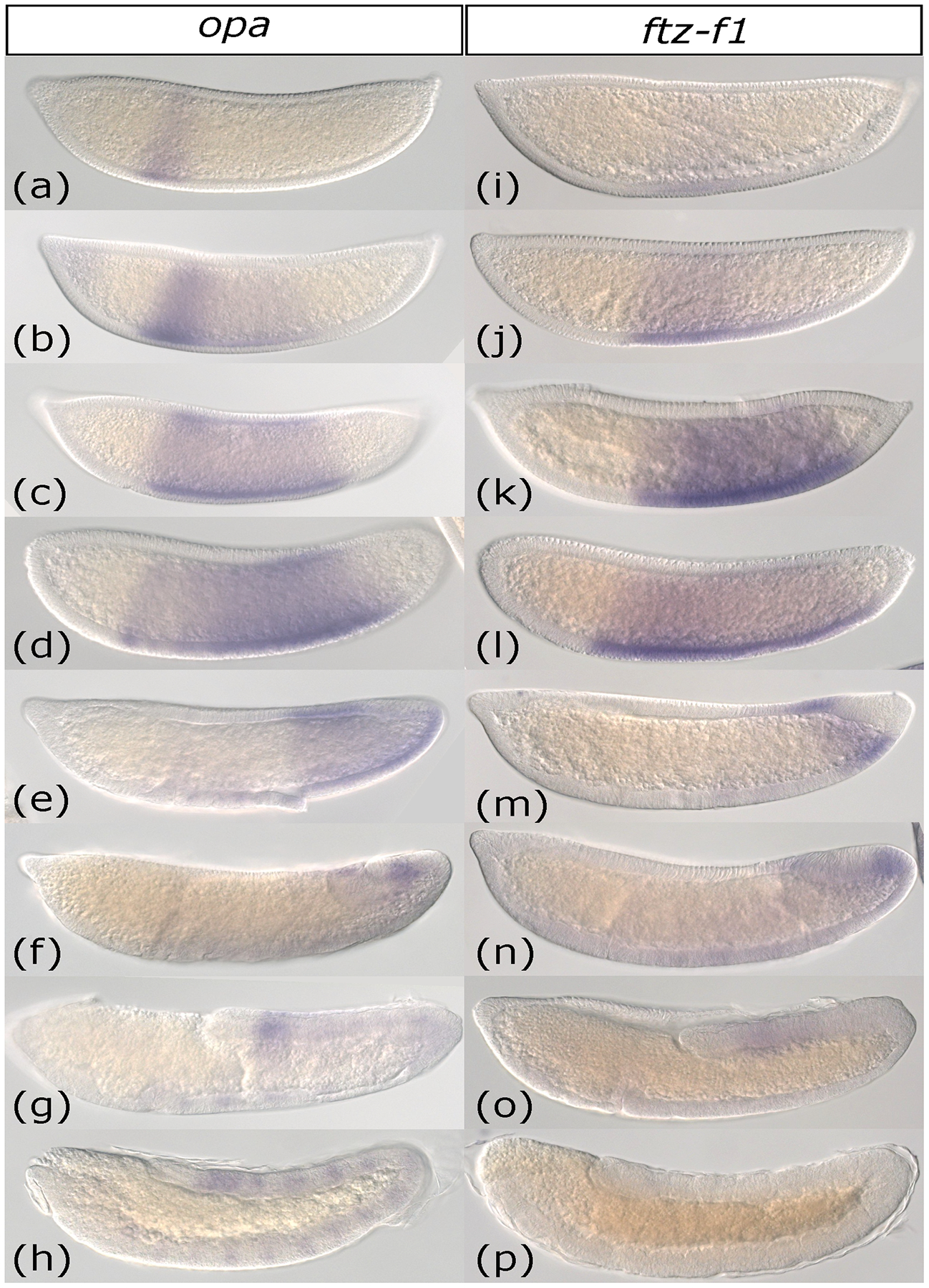
(a-h) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of odd-paired (opa) from early cellular blastoderm (a) to the end of germband extension (h). Expression is first detected as an anterior domain (a) which gradually expands posteriorly (b-c). Next, the anterior-most portion of the opa expression domain fades (d). By gastrulation, opa expression has retracted to the posterior half of the embryo (e). opa persists as a small expression domain near the posterior end of the elongating germband (f-h). Upon completion of germband extension, segmental stripes of opa appear (h). (i-p) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of ftz transcription factor-1 (ftz-f1) from early cellular blastoderm (i) to the end of germband extension (p). ftz-f1 expression begins as a faint band near the anterior of the embryo’s trunk (i). This band darkens (j) and then expands towards the posterior (k-l). ftz-f1 expression retracts posteriorly, leaving a narrow band at the posterior end of the embryo at gastrulation (m), which persists as expression near the end of the elongating germband (n-o). ftz-f1 expression completely fades by the end of germband extension (p).
Images are shown in order of increasing time. All embryos are depicted from a lateral view with the anterior on the left side.
