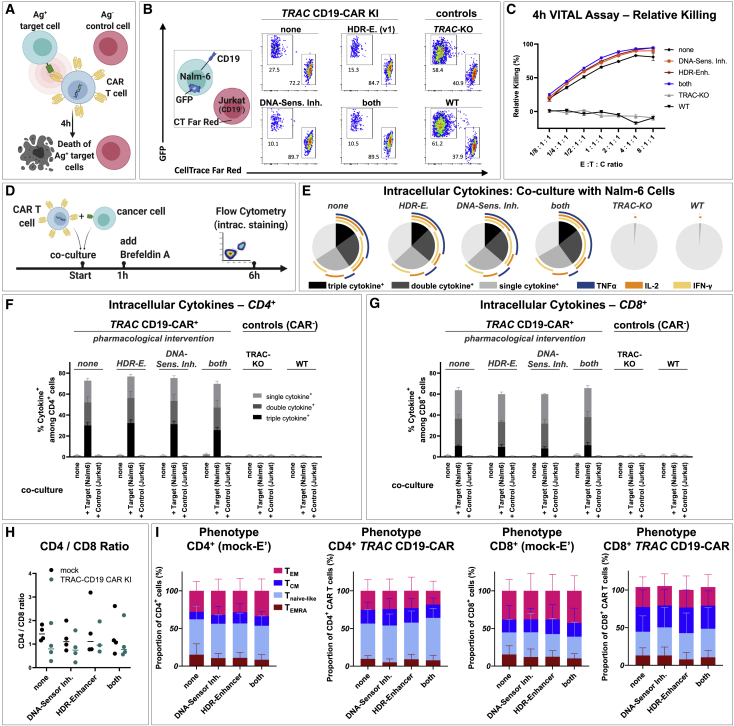
Figure 5.
Functional in vitro characterization of TRAC-integrated CD19-CAR T cells after drug-assisted gene transfer
CAR T cell generated with no drug assistance (none), with HDR enhancer (v.1) (“HDR-E.”), DNA-sensor inhibition (“HDR-Sens. Inh.”), or the combination of both approaches (both) were assessed for possible differences in cytotoxicity, cytokine production, and phenotype. (A) Experimental setup of a flow cytometric VITAL assay is shown. (B) Representative flow cytometry dot plots of viable target (T) and control (C) cells after 4 h co-culture with effecter (E) CD19-CAR T cells for the highest E:T:C ratio tested (8:1:1) are shown. Nalm-6 cells (CD19+, GFP+) served as target cells. Jurkat cells (CD19−, CellTrace Far Red labeled) served as control cells. (C) Summary of VITAL assay results as shown in (B) (n = 3 techn. replicates) is shown. (D) Experimental setup for detection of intracellular cytokines after T cell stimulation is shown. (E) Summary of intracellular cytokine staining of bulk (CAR) T cells after co-culture with CD19+ Nalm-6 cells is shown. Boolean gating was used to identify cells that produce one, two, or three of the following cytokines: interferon (IFN)-γ, IL-2, and TNFα (n = 3 donors). (F and G) Summary of intracellular cytokine staining for CD4+ (F) and CD8+ (G) (CAR) T cells alone or after co-culture with target (Nalm6) or control (Jurkat) cells is shown. (H and I) CD4/CD8 ratio (H) and summary of CAR T cell phenotype (I) on day 9 after electroporation (n = 2 donors in techn. duplicates). TEMRA: CD45RA+, CCR7−; Tnaive-like: CD45RA+ CCR7+; TCM: CD45RA, CCR7+; TEM: CD45RA−, CCR7−.