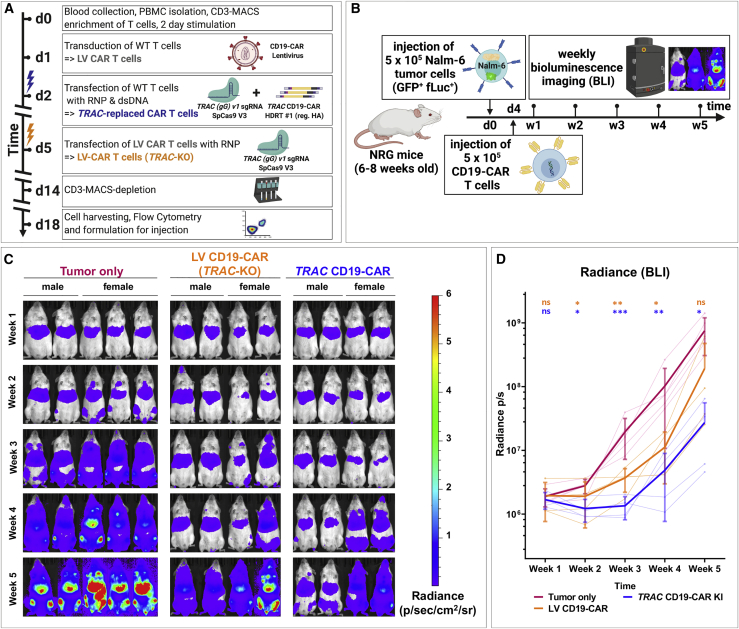
Figure 6.
Virus-free generated TRAC-replaced CAR T cells slow leukemia progression in vivo
Comparison of the therapeutic efficacies between TRAC-replaced and lentivirally transduced CD19-CAR T cells in a pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenograft mouse model. (A) Experimental setup for generation of TCR-negative CAR T cells by virus-free TRAC replacement with CD19-CAR or lentiviral transduction (LV CAR T cells) followed by TRAC-KO is shown. Prior to formulation, remaining TCR/CD3-positive T cells were depleted by MACS cell separation technology. (B) Experimental setup for Nalm-6 xenograft model. Eight-week-old Nod.Rag.Gamma (NRG) mice were challenged i.v. with 5 × 105 Nalm-6/GFP/fLuc cells. Mice not receiving leukemia (“no tumor”) were used as controls for analyses. Four days after leukemia challenge, mice were randomized among three cohorts: (1) injected i.v. with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (corresponding to the “tumor only” group), (2) injected i.v. with 5 × 105 CD19-CAR T cells generated via lentiviral transfer and consecutive TRAC KO (“LV-CD19CAR”), and (3) injected i.v. with 5 × 105 CD19-specific TCR-deficient CAR T cells generated by TRAC replacement (“TRAC CD19-CAR”). The residual CD3+ T cells were depleted from both types of CAR T cell types prior to infusion. Mice were monitored for disease severity every 2 to 3 days, and body weights were measured weekly. Leukemia engraftment, bio-distribution, and progression were assessed by weekly bioluminescence imaging (BLI) analyses. The experimental endpoint was 5 weeks after leukemia challenge. (C) BLI of all mice over a 5-week observation period is shown. BLI pictures were generated sequentially from weeks 1 to 5. Frontal pictures of mice are shown, with bioluminescence signal radiance (photons/s/cm2/sr) depicted by the color barcode on the right side. (D) Quantification of leukemia spread by BLI is shown. Radiance (photons/s) depicts each pixel summed over the regions of interest (ROIs) area containing the whole frontal side of the body. Statistical analysis comparing each cohort with the tumor only cohort at each time point was performed after log transformation using a repeated-measures two-way ANOVA with Geisser-Greenhouse correction followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.