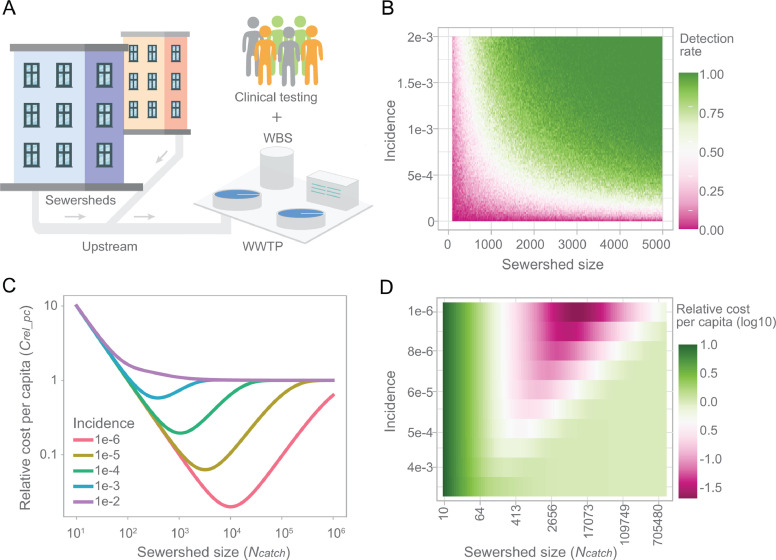
Fig. 2.
Wastewater surveillance in endemic COVID-19. (A) Schematic diagram showing the integration of upstream wastewater sampling and clinical testing for endemic COVID-19. (B) An illustration of the relationship between the sewershed size, incidence, and positive detection rate for wastewater samples, based on a previous study (Wu et al., 2021). (C-D) Cost-effectiveness through integration of wastewater surveillance and clinical tests. Both incidence and sewershed size impact the total cost for mass surveillance of viral infections in the population. A minimum cost can be achieved through strategically customizing the sewershed size for wastewater surveillance based on the infection incidence. ; the range for v is (10−6, 10−2); and range for Ncatch is (10, 106).