Fig. 1.
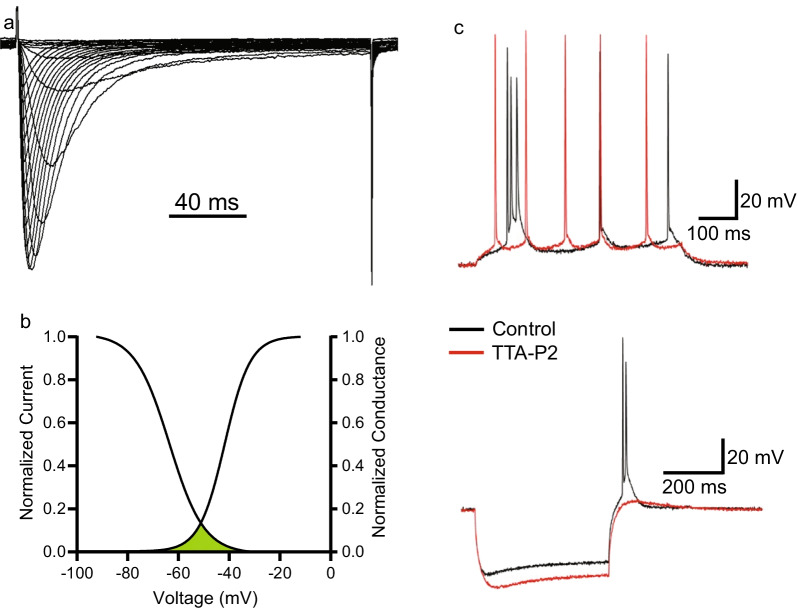
Electrophysiological properties of T-type channels. a Typical inward current recorded from T-type channels during an IV-curve. Note that inward current in response to depolarization is rapidly activating and rapidly inactivating. b Typical steady state activation and inactivation curves for T-type channels. Current activation occurs near − 60 mV and reaches peak around − 20 mV. Overlap of activation and inactivation curves reveals a significant window current between -60 and -40 mV. c Adapted with permission from Joksimovic et al. [33]. Perfusion of 10 µM TTA-P2 significantly reduces burst firing in response to current injection (top) and rebound bursting (bottom) in subicular neurons, revealing the contribution of T-type channels to activity in these neurons