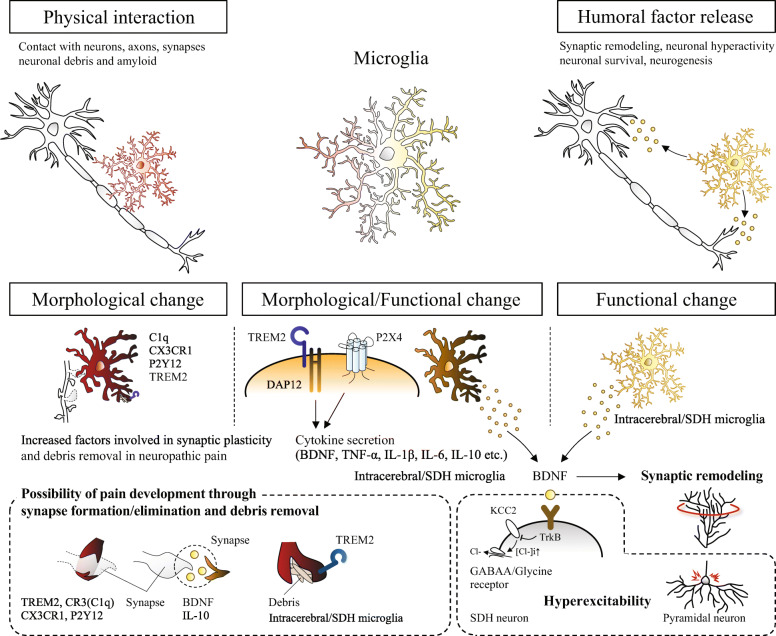
Fig. 3.
Microglial modulation of neuroplasticity in the spinal dorsal horn and S1 that underlies chronic pain after PNS or CNS injury. TOP: the physical interaction and humoral factor release. BOTTOM: morphological and functional changes in microglia after PNS or CNS injury. Studies showing morphological changes in microglia have not shown specific functions, but have suggested their involvements in the pain development based on the molecular functions. Functional changes in microglia have been suggested to be factors released via TREM2/DAP12 or P2X4 signals. BDNF is one factor shown to be secreted from microglia in the spinal cord and brain after PNS or CNS injury, involved in pain development through synaptic remodeling and inducing hyperexcitability