Fig. 7.
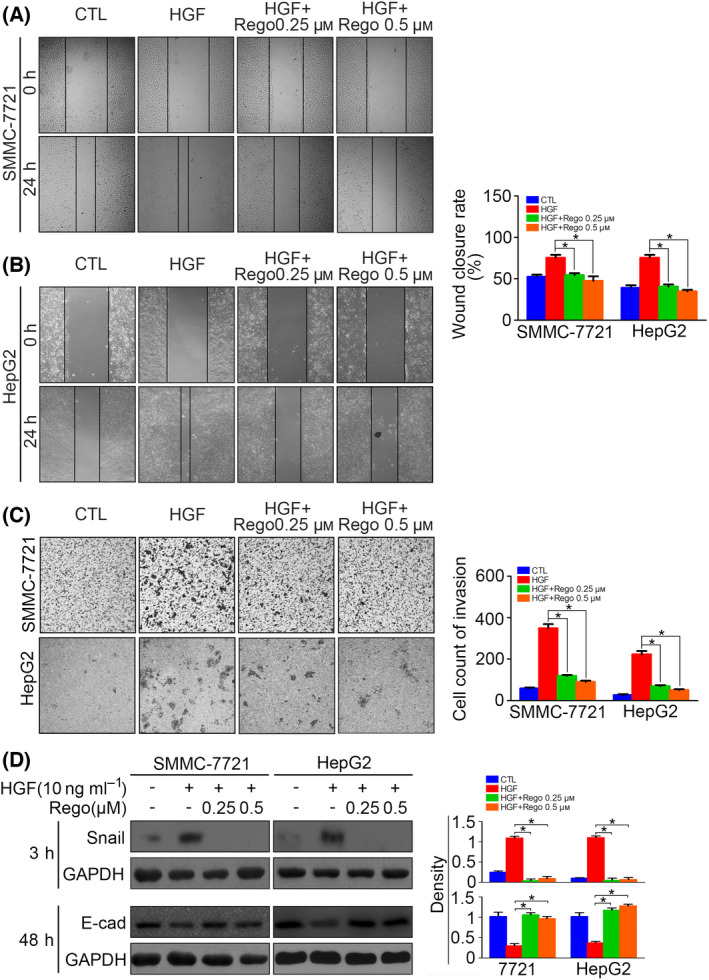
Regorafenib inhibits EMT by downregulating Snail in HCC cells. (A) Serum‐starved SMMC‐7721 cells preincubated with regorafenib (0.25 μm or 0.5 μm) for 6 h were treated with HGF (10 ng·mL−1) for 24 h, and cell migration was determined by a wound‐healing assay. (B) Serum‐starved HepG2 cells preincubated with regorafenib (0.25 μm or 0.5 μm) for 6 h were treated with HGF (10 ng·mL−1) for 24 h, and cell migration was determined by a wound‐healing assay. (C) Serum‐starved SMMC‐7721 and HepG2 cells preincubated with regorafenib (0.25 μm or 0.5 μm) for 6 h were treated with HGF (10 ng·mL−1) for 24 h, and cell invasion was determined by a transwell assay. This is the same experiment as that presented in Figure 2B, and the control presented for the HepG2 cells is the same between these two figures. (D) Serum‐starved SMMC‐7721 and HepG2 cells preincubated with regorafenib (0.25 μm or 0.5 μm) for 6 h were treated with HGF (10 ng·mL−1) for 1 h, and Snail was detected 3 h after treatment, whereas E‐cadherin was detected 48 h after treatment, by western blotting. The density of each band was normalized to GAPDH (*P < 0.05). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD from three individual experiments. Differences between groups were determined using the Student's t‐test and two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction.
