Figure 1.
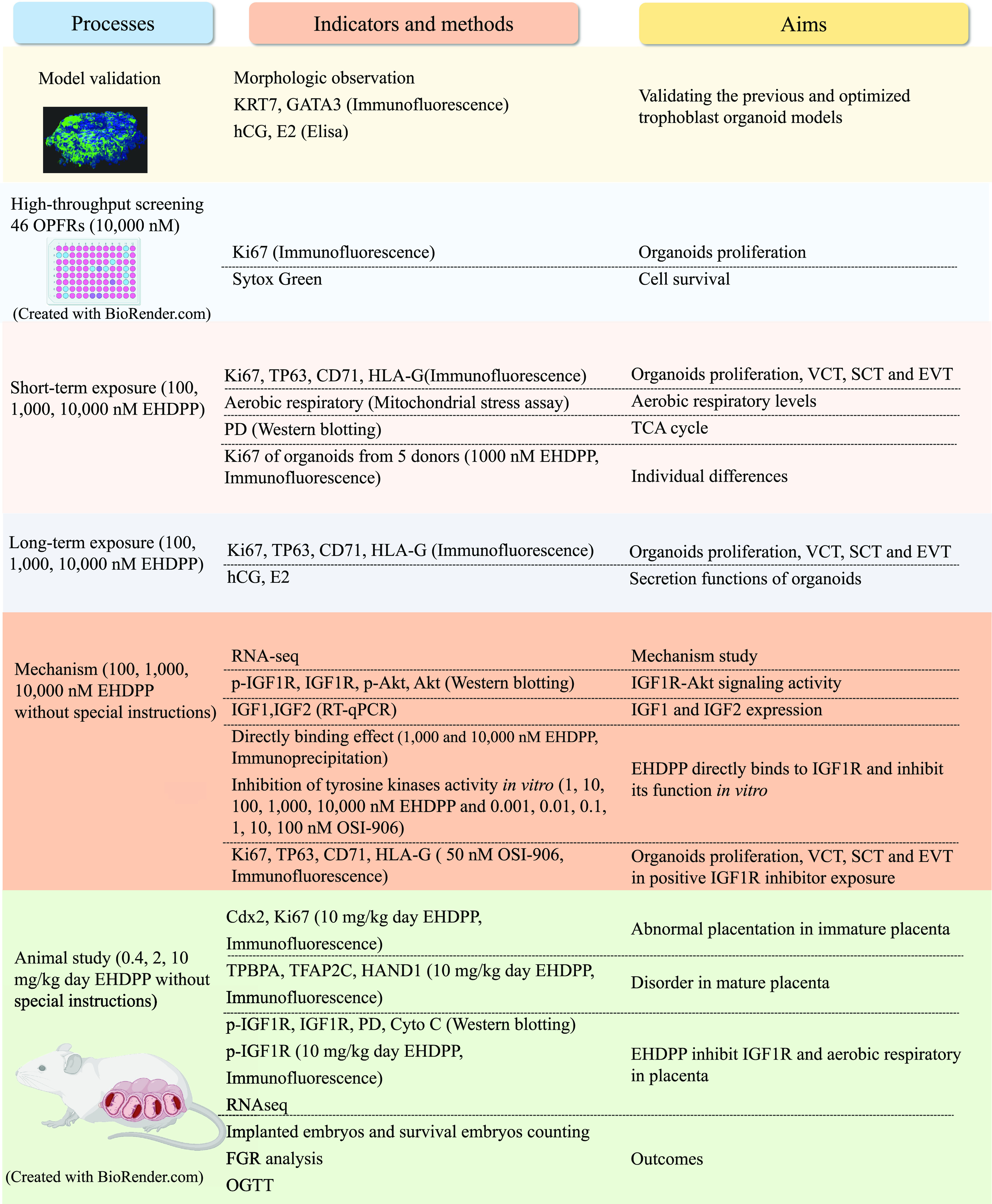
Summary of methods. Note: Akt, protein kinase B; CD71, transferrin receptor; Cyto C, cytochrome C; , estradiol; EHDPP, 2-ethylhexyl-diphenyl phosphate; EVT, extravillous trophoblast cell; FGR, fetal growth restriction; GATA3, GATA-binding protein 3; HAND1, crest derivatives-expressed protein 1; hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin; HLA-G, human leukocyte antigen protein-G; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; KRT7, keratin 7; OGTT, oral glucose tolerance test; OPFRs, organophosphate flame retardants; OSI-906, linsitinib; p-Akt, phosphorylated Akt; PD, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; p-IGF1R, phosphorylated IGF1R; RNA-seq, RNA sequencing; SCT, syncytiotrophoblast; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; TFAP2C, transcription factor ; TP63, tumor protein 63; TPBPA, trophoblast-specific ; VCT, villous cytotrophoblast.
